New publication in eLife of the Jordan Lab in collaboration with the IBMB Imaging Platform showing that…
PHF8 histone demethylase regulates astrocyte differentiation and function
PHF8 demethylates H4K20me at astrogenic and synaptogenic genes during astrocyte differentiation. Accordingly, astrocytic-PHF8 depletion has a striking effect on neuronal synapse formation and maturation.
Epigenetic factors have been shown to play a crucial role in X-linked intellectual disability (XLID). Here, we investigate the contribution of the XLID-associated histone demethylase PHF8 to astrocyte differentiation and function. Using genome-wide analyses and biochemical assays, we reveal a regulatory crosstalk between PHF8 and Notch signaling pathway that balances the expression of the master astrocytic gene Nfia. Moreover, PHF8 regulates key synaptic genes in astrocytes by keeping low levels of H4K20me3. Accordingly, astrocytic-PHF8 depletion has a striking effect on neuronal synapse formation and maturation in vitro. These data reveal that PHF8 is crucial in astrocyte development to maintain the chromatin homeostasis and limiting the heterochromatin formation at synaptogenic genes. Our studies suggest a new paradigm for the implication of epigenetics in intellectual disability.
Reference:
Iacobucci S, Padilla N*, Gabrielli M*, Navarro C, Lombardi M, Vicioso-Mantis M, Verderio C, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. (2021) Development. June 3;194951.
DOI: 10.1242/dev.194951.
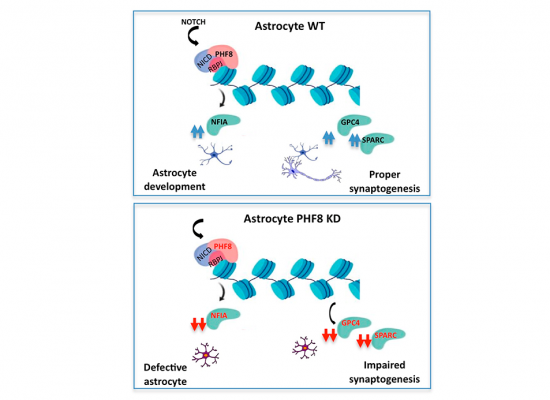
PHF8 directly regulates the expression of the master regulator of astrocyte differentiation Nfia as well as genes involved in synapses. Depletion or alteration of PHF8 catalytic activity leads to defective astrocytes that are deficient in synaptic function.