Lab presentation
During neurogenesis a delicate balance between stability and plasticity is essential; in one sense, stability to allow the pool of neural progenitor cells to proliferate and propagate the cell identity to daughter cells; and plasticity to provide a window to modify this identity and allow differentiation. This balance is preserved by the coordinated action of epigenetic regulators and transcription factors that respond to developmental signals.
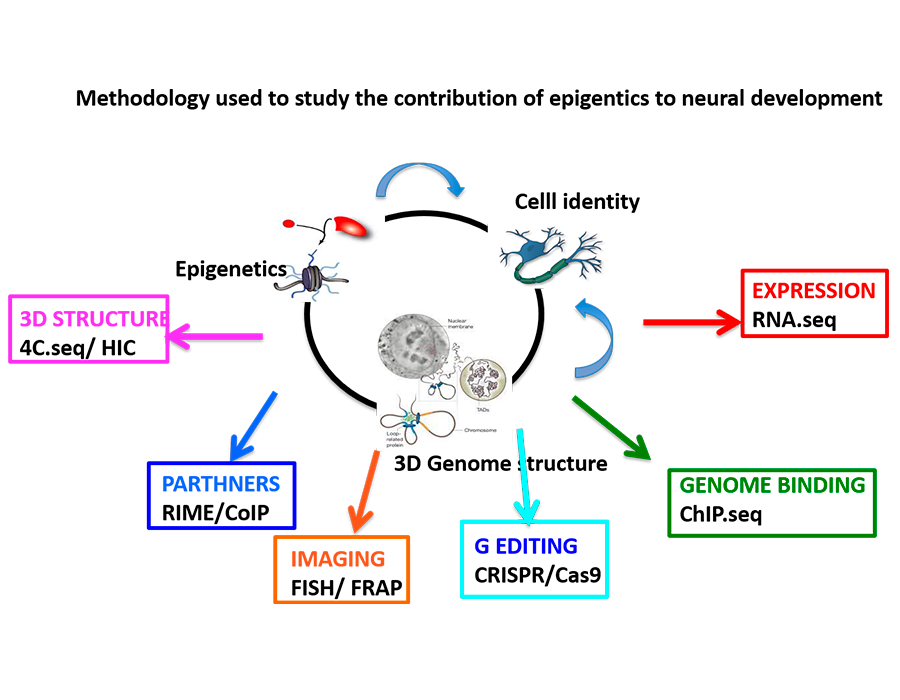
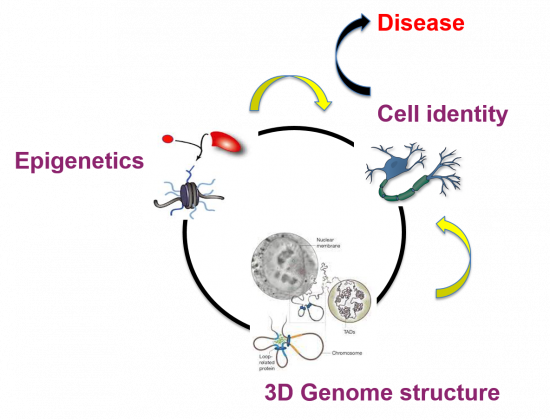
Our group is focused on understanding the role of epigenetics in gene transcription during neurogenesis. The final goal is to define the principles that control the activity of our genome to establish and maintain the cell identity during early neurogenesis. We study mechanisms of gene expression at different levels, from the action of epigenetic regulators, their interplay with developmental signals, to how the genomic loci are positioned in the 3D space within cell nuclei.
Moreover, epigenetic alterations are common in a wide spectrum of diseases, from developmental disorders to many types of cancers. With our studies we expect to pave the way towards deeper understanding on how deregulation of these epigenetic factors leads to disease focusing in intellectual disability, helping to develop therapeutic and diagnostic tools.

Projects
EPIGENETIC DEFECTS IN MENTAL RETARDATION
A very high number of genes mutated in mental retardation encode regulators of chromatin structure. One of these genes is PHF8, a histone demethylase enzyme. The PHF8 function and the molecular mechanisms responsible for its role in mental retardation are not clearly established. In the laboratory we are interested in unraveling the role of PHF8 in vivo.
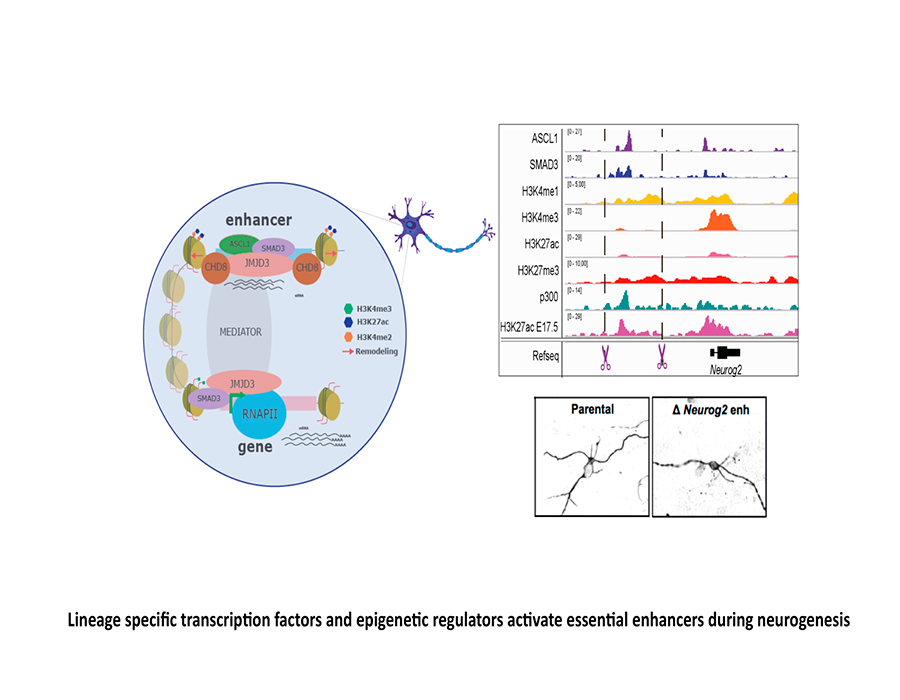
THE ROLE OF HISTONE METHYLATION DURING NEUROGENESIS
Neural differentiation requires general changes in gene expression in which epigenetic factors are involved. Our work has identified several signalling pathways that cooperate with the enzymes responsible of H3K27me3 to control neurogenesis. Our goal is to describe the molecular mechanisms responsible of this cooperation using the chicken neural tube and neural stem cells as models.
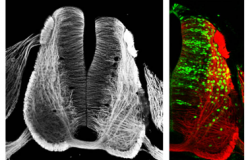
GENOME ARCHITECTURE AND CELL IDENTITY
Long-range gene regulation works through chromatin looping mechanisms that bring together the promoters of genes with distant regulatory regions. In addition, enhancers also co-associate with other enhancers in 3D space that change during development and that will facilitate their activation. We are studying how epigenetic regulators (JMJD3 and PHF2) integrate with developmental signals to modify the genome architecture, in particular the formation of enhancer-clusters and the lamina anchorage.
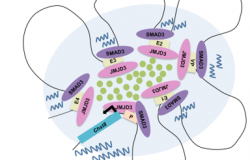
Our strategy for unraveling the principles of genome function in development aims to integrate cellular and molecular biology, epigenetics, nuclear imaging and proteomics technologies.
Lab people

Marian Martínez
Principal investigator
Graduated in pharmacology from the Santiago de Compostela University. Marian
Martínez-Balbás obtained her PhD at the Polytechnic University of Barcelona studying
DNA and chromatin structure. She was a postdoctoral Fellow at the NIH (USA) where
she focused on chromatin remodeling and dynamics at Dr C Wu’s laboratory. She then
moved to Cambridge (UK) to the J Gurdon Institute (to the group of Dr T Kouzarides) to
study the contribution of epigenetics mechanisms to cell cycle progression, cell
proliferation and development.
In 2000 she got a permanent CSIC position at the IBMB to start a new group. Her research investigation is focused on understanding the role of several chromatin regulators controlling the transcriptional program during development in a cell-type specific manner.
Her group analyzes different aspects of chromatin dynamics during neurogenesis using in vitro (neural stem cells) and in vivo models (chicken neural tube) in physiological and pathological conditions, focusing in the role of epigenetics in intellectual disability.
Past students
Stella Pappa
Simona Iacobucci
Marta Vicioso
Elena Álvarez de la Campa
Raquel Fueyo
Maria Alejandra Garcia
Arnau Noguera Segura
Selected publications
Gracia-Diaz C et al (2023) Gain and loss of function variants in EZH1 disrupt neurogenesis and cause dominant and recessive neurodevelopmental disorders. Nature Communications, 14(1):4109. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39645-5.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-39645-5
Vicioso-Mantis M, Martínez-Balbás MA (2022). Spatial genome organization, TGFβ, and biomolecular condensates: Do they talk during development? BioEssays 17:e2200145. DOI: 10.1002/bies.202200145
http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/bies.202200145
Vicioso-Mantis M, Aguirre S, Martínez-Balbás MA. JmjC family of histone demethylases form nuclear condensates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23(14):7664. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147664.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/14/7664
Vicioso-Mantis M *, Fueyo R*, Navarro C, Cruz-Molina S, van Ijcken W FJ, Rebollo E, Rada-Iglesias A, and Martínez-Balbás MA (2022) JMJD3 intrinsically disordered region links the 3D-genome structure to TGFβ-dependent transcription activation. Nature Communications. 13(1):3263.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-30614-y
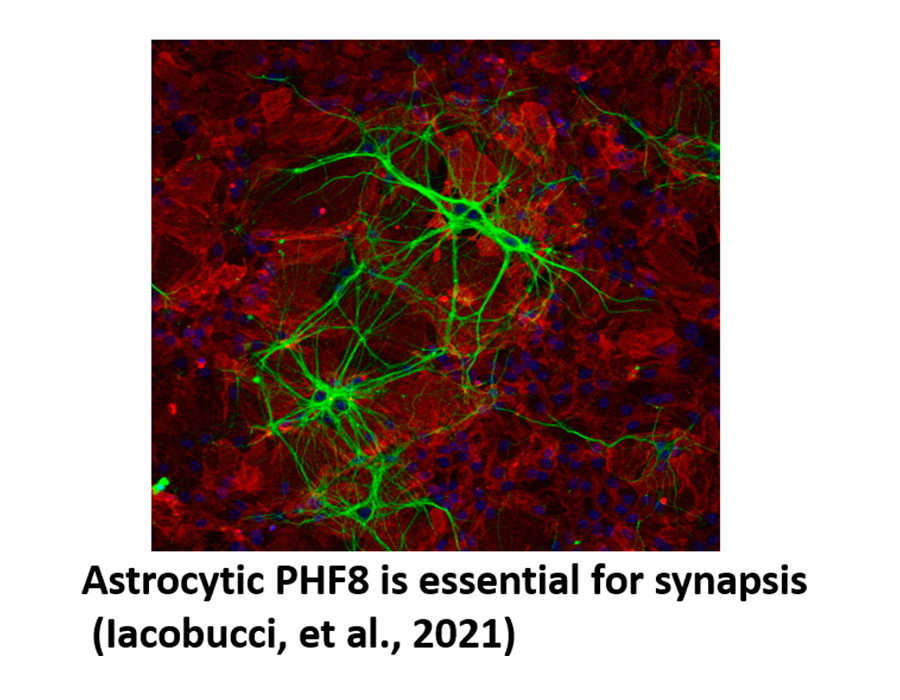
Iacobucci S, Padilla N, Gabrielli M, Navarro C., Lombardi M, Vicioso-Mantis M, Verderio C, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. (2021) The histone demethylase PHF8 regulates astrocyte differentiation and function. Development, 148, dev194951.
https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article-abstract/148/12/dev194951/269266/
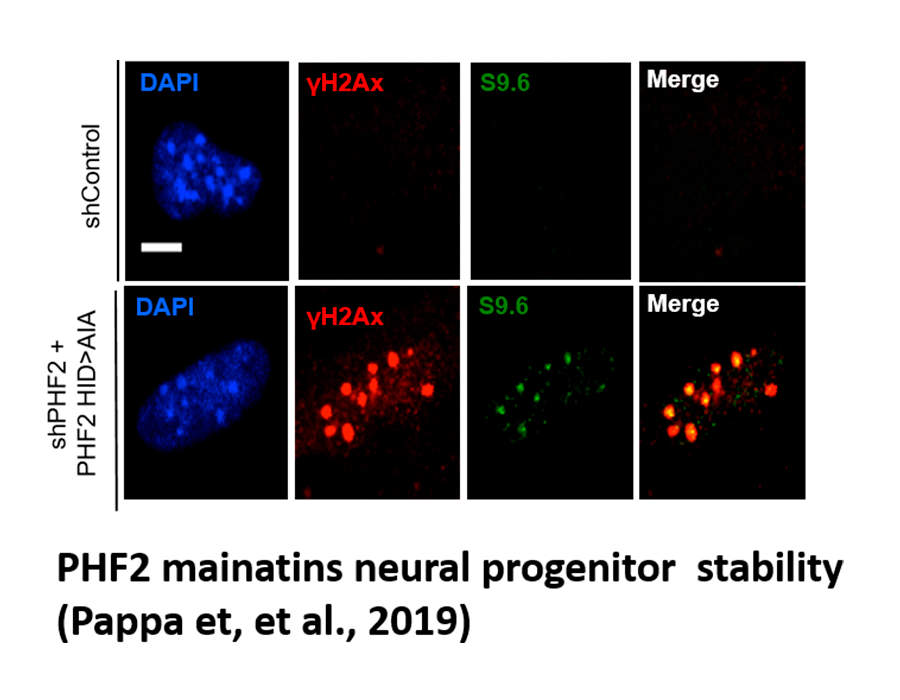
Pappa S, Padilla N, Iacobucci S, Vicioso M, Álvarez de la Campa E, Navarro C, Marcos E, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. (2019) PHF2 histone demethylase prevents DNA damage and genome instability by controlling cell cycle progression of neural progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A;116, 19464-19473.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1903188116
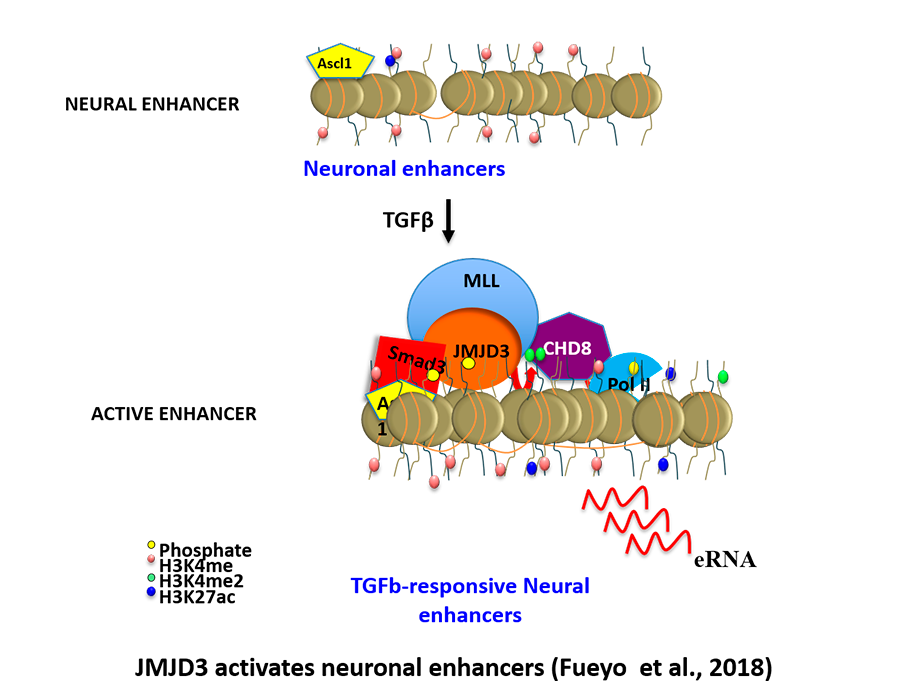
Fueyo R, Iacobucci S, Pappa S, Estarás C, Lois S, Vicioso-Mantis M, Navarro C, Cruz-Molina S, Reyes JC, Rada-Iglesias Á, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás M.A. (2018) Lineage specific transcriptio factors and epigenetic regulators mediate TGFb-dependent enhancer activation. Nucleic Acids Research. 46,3351-3365.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29438503
Le Dréau G, Escalona R, Fueyo R, Herrera A, Martínez JD, Usieto S, Menendez A, Pons S, Martinez-Balbas MA, Marti. 2018 E proteins sharpen neurogenesis by modulating proneural bHLH transcription factors activity in an E-box-dependent manner. Elife. pii: e37267.
https://elifesciences.org/articles/37267
Asensio-Juan E, Fueyo R, Pappa E, Iacobucci S, Badosa C, Lois S, Balada M, Bosch-Presegué L, Vaquero A, Gutiérrez S, Caelles C, Gallego C, de la Cruz X, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2017) The histone demethylase PHF8 is a molecular safeguard of the IFNγ response. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, 3800-3811.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1346
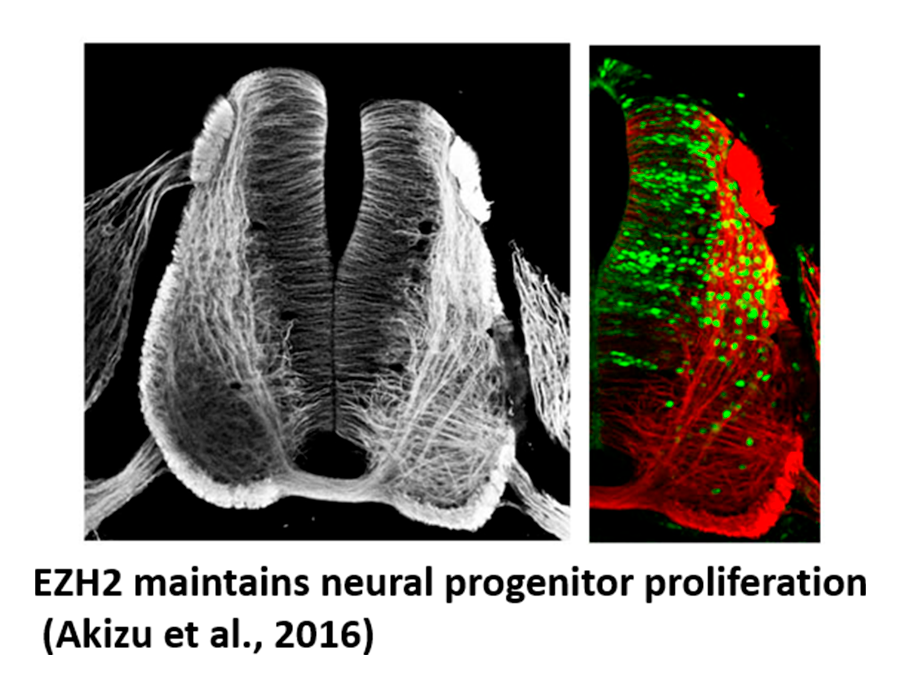
Akizu N, García MA, Estarás C, Fueyo R, de la Cruz, X, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2016). EZH2 regulates neuroepithelium structure and neuroblast proliferation by repressing p21. Open Biology, 4, 150227.
http://rsob.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/royopenbio/6/4/150227.full.pdf
Sánchez-Molina S, Estarás C, Oliva JL, Akizu N, Asensio-Juan E, Rojas JM, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2014) Regulation of CBP and Tip60 coordinates histone acetylation at local and global level during Ras induced transformation. Carcinogenesis, 35: 2194-2202.
https://academic.oup.com/carcin/article/35/10/2194/322625
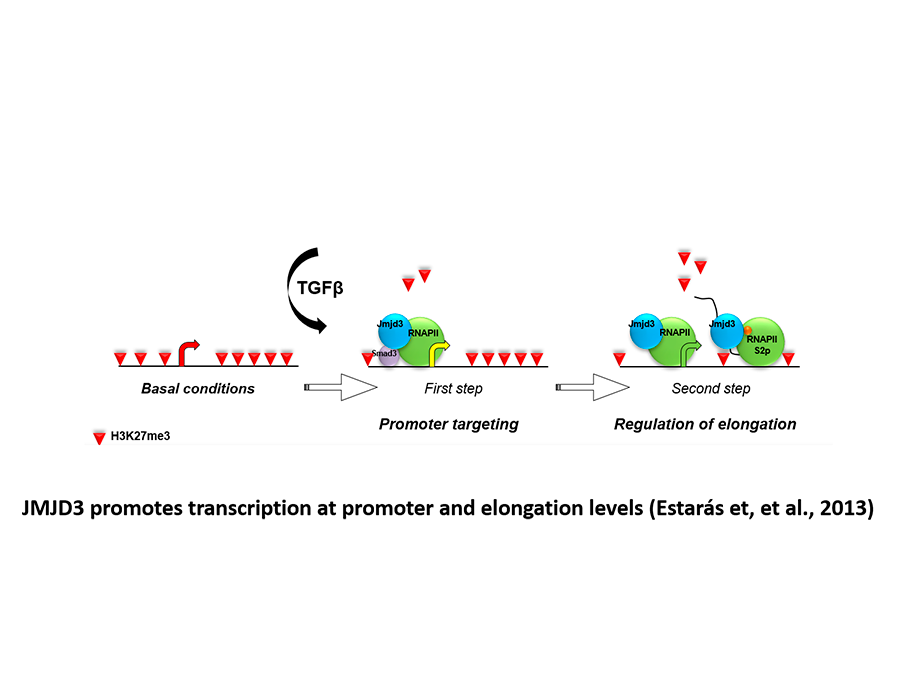
Estarás C, Fueyo R, Akizu N, Beltrán S, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2013) RNA polymerase progression through H3K27me3-enriched gene bodies require JMJD3 histone demethylase. Molecular Biology Cell, 24: 351-360. Highligted in MBC.
https://www.molbiolcell.org/doi/pdf/10.1091/mbc.E12-07-0561
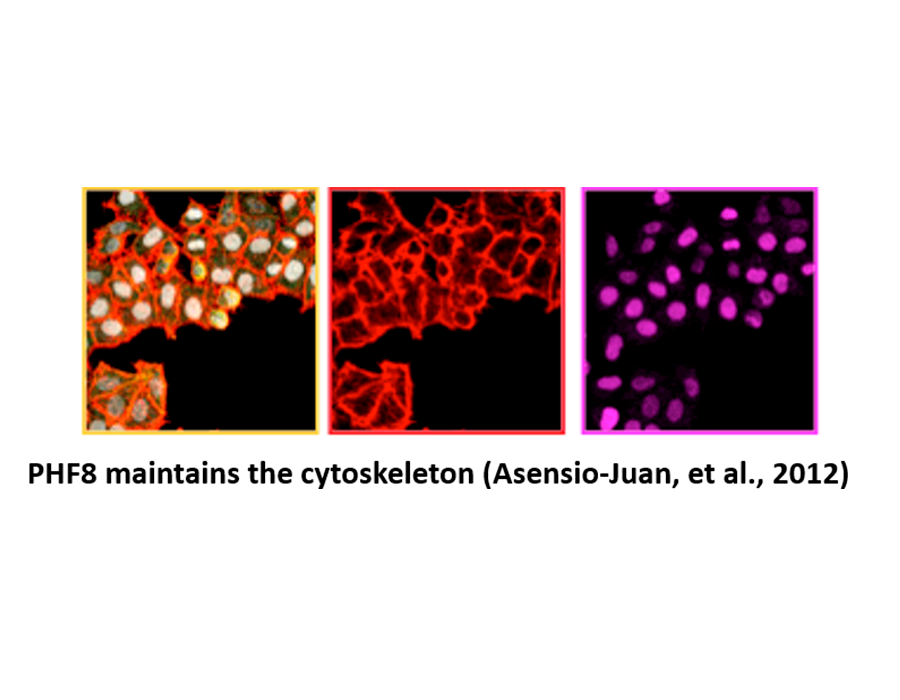
Asensio-Juan E, Gallego C, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2012) Histone demethylase PHF8 is essential for cytoskeleton dynamics. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 9429-9440.
https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/40/19/9429/2414741
Estarás C, Akizu N, García MA, de la Cruz, X, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2012) Genome-wide analysis reveals that Smad3 and JMJD3 HDM co-activate the neural developmental program. Development, 139, 2681-2691.
https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article/139/15/2681/45112/
All publications
Gracia-Diaz C et al (2023) Gain and loss of function variants in EZH1 disrupt neurogenesis and cause dominant and recessive neurodevelopmental disorders. Nature Communications, 14(1):4109. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39645-5.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-39645-5
Vicioso-Mantis M, Aguirre S, Martínez-Balbás MA. JmjC family of histone demethylases form nuclear condensates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23(14):7664. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147664.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-
Vicioso-Mantis M *, Fueyo R*, Navarro C, Cruz-Molina S, van Ijcken W FJ, Rebollo E, Rada-Iglesias A, and Martínez-Balbás MA (2022) JMJD3 intrinsically disordered region links the 3D-genome structure to TGFβ-dependent transcription activation. Nature Communications. 13(1):3263.
https://www.nature.com/
Vicioso-Mantis M, Martínez-Balbás MA (2022). Spatial genome organization, TGFβ, and biomolecular condensates: Do they talk during development? BioEssays 17:e2200145. DOI: 10.1002/bies.202200145
http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/bies.202200145
Iacobucci S, Padilla N, Gabrielli M, Navarro C., Lombardi M, Vicioso-Mantis M, Verderio C, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. (2021) The histone demethylase PHF8 regulates astrocyte differentiation and function. Development, 148, dev194951.
https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article-abstract/148/12/dev194951/269266/
Pappa S, Padilla N, Iacobucci S, Vicioso M, Álvarez de la Campa E, Navarro C, Marcos E, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. (2019) PHF2 histone demethylase prevents DNA damage and genome instability by controlling cell cycle progression of neural progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A;116, 19464-19473.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1903188116
Le Dréau G, Escalona R, Fueyo R, Herrera A, Martínez JD, Usieto S, Menendez A, Pons S, Martinez-Balbas MA, Marti. 2018 E proteins sharpen neurogenesis by modulating proneural bHLH transcription factors activity in an E-box-dependent manner. Elife. pii: e37267.
https://elifesciences.org/articles/37267
Fueyo R, Iacobucci S, Pappa S, Estarás C, Lois S, Vicioso-Mantis M, Navarro C, Cruz-Molina S, Reyes JC, Rada-Iglesias Á, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás M.A. (2018) Lineage specific transcriptio factors and epigenetic regulators mediate TGFb-dependent enhancer activation. Nucleic Acids Research. 46,3351-3365.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29438503
Asensio-Juan E, Fueyo R, Pappa E, Iacobucci S, Badosa C, Lois S, Balada M, Bosch-Presegué L, Vaquero A, Gutiérrez S, Caelles C, Gallego C, de la Cruz X, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2017) The histone demethylase PHF8 is a molecular safeguard of the IFNγ response. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, 3800-3811.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1346
Sánchez-Cid L, Pons M, Lozano JJ, Rubio N, Guerra-Rebollo M, Soriano A, Paris-Coderch L, Segura MF, Fueyo R, Arguimbau J, Zodda E, Bermudo R, Alonso I, Caparrós X, Cascante M, Rafii A, Kang Y, Martínez-Balbás MA, Weiss SJ, Blanco J, Muñoz M, Fernández PL, Thomson TM. MicroRNA-200, associated with metastatic breast cancer, promotes traits of mammary luminal progenitor cells. (2017) Oncotarget, 8, 83384-83406.
https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20698
García MA, Fueyo R, Martínez-Balbás MA. Lysine demethylases: structure, function and disfunction (2016) Título del libro: “Chromatin signaling”. Editorial: Elsevier. Editores: O. Binda y M.E. Fernández-Zapico. eBook ISBN: 9780128026090. Hardcover. ISBN: 9780128023891.
https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802389-1.00010-1
Akizu N, García MA, Estarás C, Fueyo R, de la Cruz, X, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2016). EZH2 regulates neuroepithelium structure and neuroblast proliferation by repressing p21. Open Biology, 4, 150227.
http://rsob.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/royopenbio/6/4/150227.full.pdf
Akizu N, Martínez-Balbás MA. EZH2 orchestrates apicobasal polarity and neuroepithelial cell renewal. Comment (2016) Neurogenesis, Published Online: 17 Nov 2016.
https://doi.org/10.1080/23262133.2016.1250034
Fueyo R,*, García MA,* Martínez-Balbás MA. Jumonji family histone demethylases in neural development (Requested Review) (2015) Cell and Tissue Research, 359, 87-98. * Equally contributing authors
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1924-7
Petazzi P,* Akizu N,* García MA, Estarás C, Martínez de Paz A, Rodriguez-Paredes M, Martínez-Balbás MA, Huertas D, Esteller M. An increase in MECP2 dosage impairs neural tube formation. (2014) Neurobiology of Disease, 67:49-56. * Equally contributing authors
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.03.009
Sánchez-Molina S, Estarás C, Oliva JL, Akizu N, Asensio-Juan E, Rojas JM, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2014) Regulation of CBP and Tip60 coordinates histone acetylation at local and global level during Ras induced transformation. Carcinogenesis, 35: 2194-2202.
https://academic.oup.com/carcin/article/35/10/2194/322625
Vidal-Laliena M, Gallastegui E, Mateo F, Martínez-Balbás MA, Pujol MJ, Bachs O. HDAC3 regulates cyclin A stability. (2013) Journal of Biological Chemistry 288, 21096-21104.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m113.458323
Estarás C, Fueyo R, Akizu N, Beltrán S, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2013) RNA polymerase progression through H3K27me3-enriched gene bodies require JMJD3 histone demethylase. Molecular Biology Cell, 24: 351-360. Highligted in MBC.
https://www.molbiolcell.org/doi/pdf/10.1091/mbc.E12-07-0561
Asensio-Juan E, Gallego C, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2012) Histone demethylase PHF8 is essential for cytoskeleton dynamics. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 9429-9440.
https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/40/19/9429/2414741
Estarás C, Akizu N, García MA, de la Cruz, X, and Martínez-Balbás MA. (2012) Genome-wide analysis reveals that Smad3 and JMJD3 HDM co-activate the neural developmental program. Development, 139, 2681-2691.
https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article/139/15/2681/45112/
Celià T, Meca-Cortés O, Martínez-Paz A, Mateo F, Ulloa C, Rubio N, Arnal A, Estarás C, Lozano JJ, Bermudo R, García de Herreros A, Martínez-Balbás MA, Millà J, Vilella R, Gomis R, Blanco -Fernández PL, Thomson TM. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition can suppress major attributes of epithelial tumor-initiating cells. (2012) Journal of Clinical Investigation, 122, 1849-1868.
https://doi.org/10.1172/jci59218
Perez-Luna M, Aguasca M, Perearnau A, Serratosa J, Martínez-Balbás MA, Pujol MJ Bachs O. PCAF regulates the stability of the transcriptional regulator and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Regulation of p27Kip1. (2012) Nucleic Acid Research, 40, 6520-6533.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks343
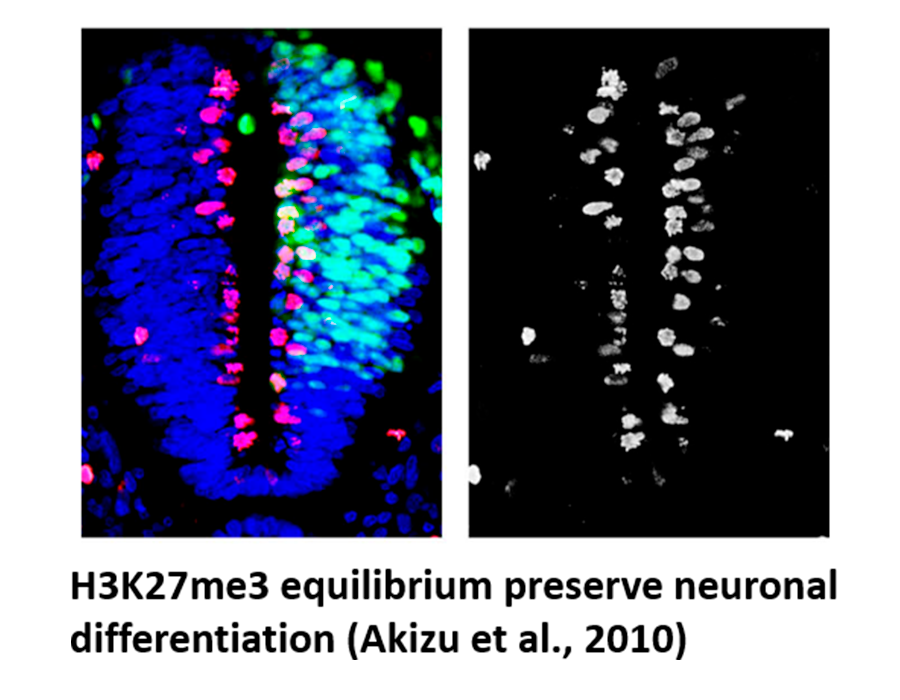
Akizu, N, Estarás C, Guerrero L, Martí E, Martínez-Balbás MA. H3K27me3 regulates BMP activity in developing spinal cord. (2010) Development, 137, 2915-2925. Highligted in Development 137:e1702: “Spinal cord development BuMPs into chromatin” and Published in Articles of Interest in Other COB Journals – From Development (2010). Journal of Cell Science 123:e1; doi:10.1242/jcs.079251
https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.049395
Lois S, Akizu N, Martínez-Balbás MA, de la Cruz X. Characterization of structural variability sheds light on the specificity determinants of the interaction between effector domains and histone tails. (2010) Epigenetics, 5, 137-148. *COVER PICTURE
https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.5.2.11079
Mateo F, Vidal-Laliena M, Canela N, Zecchin A, Martínez-Balbás MA, Agell, N, Giacca M, Pujol MJ, Bachs O. The transcriptional co-activator PCAF regulates cdk2 activity. (2009) Nucleic Acids Reseach, 37, 7072-7084.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp777
Mateo F, Vidal-Laliena M, Canela N, Busino L, Martínez-Balbás MA, Pagano M, Agell N, Bachs O. Degradation of cyclin A is regulated by acetylation. (2009) Oncogene, 28, 2654-2666.
https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.127
Blanco-García N, Asensio-Juan E, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. Autoacetylation regulates P/CAF nuclear localization. (2009) Journal of Biological Chemistry , 284, 1343-1352.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m806075200
Valls E, Blanco N, Aquizu N, Piedra D, Estarás C, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. Involvement of chromatin and histone deacetylation in the SV40 T antigen transcription regulation. (2007) Nucleic Acids Research, 35, 1958-1968.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl1113
LLois S, Blanco N, Martínez-Balbás MA*, de la Cruz X*. The functional modulation of epigenetic regulators by alternative splicing (2007) BMC Genomics, 8, 252-266. *CO-CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-252
Sánchez-Molina S, Oliva JL, García-Vargas S, Valls E, Rojas JM, Martínez-Balbás, MA. The histone acetyltransferases CBP/p300 are degraded in NIH 3T3 cells by activation of Ras signalling pathway. (2006) Biochemical Journal, 398, 215-224.
https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20060052
De la Cruz X, Llois S, Sánchez-Molina S, Martínez-Balbás MA. Do protein motifs read the histone code? (2005) BioEssays, 27 (2) 164-175.
https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20176
Valls E, Sánchez-Molina S, Martínez-Balbás MA. Role of histone modifications in marking and activating genes through mitosis. (2005) Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 42592-42600.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507407200
Valls E, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. The SV40 T antigen modulates CBP histone acetyltransferase activity. (2003) Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3114-3122.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg418
Santos-Rosa H, Valls E, Kouzarides T, Martínez-Balbás MA. Mechanisms of P/CAF auto-acetylation. (2003) Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 4285-4292.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg655
Martínez-Balbás MA, Bauer UM, Nielsen SJ, Brehm A, Kouzarides T. Regulation of E2F1 activity by acetylation. (2000) The EMBO Journal, 19, 662-671.
https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.4.662
Martínez-Balbás MA, Tsukiyama T, Wu C. Drosophila NURF-55, a WD repeat protein involved in histone metabolism. (1998) PNAS, 95, 132-137.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.1.132
Wu C, Tsukiyama T, Gdula D, Georgel P, Martínez-Balbás MA, Mizuguchi G, Ossipow V, Sandaltzopoulos R, Wang HM. ATP-dependent Remodeling of Chromatin. (1998) Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on quantitative Biology. Vol LXIII, 525-534.
http://symposium.cshlp.org/content/63/525
Martínez-Balbás MA, Bannister A, Martin K, Haus-Seuffert P, Meisterernst M, Kouzarides T. The acetyltransferase activity of CBP stimulates transcription. (1998) The EMBO Journal, 17, 2886-2893.
https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.10.2886
Reid J, Bannister A, Zegerman P, Martínez-Balbás MA, Kouzarides T. E1A directly binds and regulates the P/CAF acetyltransferase. (1998) The EMBO Journal, 17, 4469-4477.
https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.15.4469
Espinás ML, Jiménez-García E, Martínez-Balbás MA, Azorín F. Formation of triple-stranded DNA at d(GA.TC)n sequences prevents nucleosome assembly and is hindered by nucleosomes. (1996) Journal of Biological Chemistry , 271, 31807-31812.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.50.31807
Martínez-Balbás MA, Jiménez-García E, Azorín F. Zinc selectively interacts with DNA sequences essential for the binding of the zinc finger transcription factor TFIIIA to the 5S-RNA gene. (1995) Nucleic Acids Research, 23, 2464-2471.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/23.13.2464
Martínez-Balbás MA, Dey A, Rabindran SR, Ozato K, Wu C. Displacement of sequence-specific transcription factors from mitotic chromatin. (1995) Cell, 83, 29-38.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90231-7
Martínez-Balbás MA. Reversion of a SV40 enhancer mutant depends on the growth conditions. (1994) Gene, 139, 211-214.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(94)90757-9
Beltrán R,* Martínez-Balbás MA*, Bernues J, Murdrie A, Lilley D, Azorín F. Characterization of the zinc-induced structural transition to H*-DNA at a d(CT/GA)22 sequence. (1993) Journal of Molecular Biology, 230, 966-978. * EQUALLY CONTRIBUTING AUTHORS
https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1993.1213
Martínez-Balbás MA, Azorín F. The effect of zinc on the secondary structure of the d(GA.CT)n DNA sequences of different length: a model for the formation H*-DNA. (1993) Nucleic Acids Research, 21, 2557-2562.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/21.11.2557
De la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA, Tormo J, Verdaguer N. Crystal and Molecular structure of 2-oxo-1-Pyrrolidine Acetamide Copper Perchlorate Monohydrate. (1992) Acta Cryst, C48, 118-121.
Azorín F, Beltrán R, Casasnovas JM, Bernues J, Martínez-Balbás MA, Huertas A, Ortiz M. Structural polymorphism of d(CT/GA)n sequences: The effect of zinc ions. (1992) Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 16E, 126, R 101.
Carrera P, Martínez-Balbás MA, Portugal J, Azorín F. Identification of sequence elements contributing to the intrinsic curvature of the mouse satellite DNA repeat. (1991) Nucleic Acid Research 19, 5639-5644.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/19.20.5639
Martínez-Balbás MA, Rodríguez-Campos A, García-Ramirez M, Saínz J, Carrera P, Aymamí J, Azorín F. Satellite DNA contain sequences which induce curvature. (1990) Biochemistry, 29, 2342-2348.
https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00461a019
Pons M, Campayo L, Martínez-Balbás MA, Azorín F, Navarro P, Giralt E. A new ionizable chromophore of 1,4-bis (alkylamino) benzo (G) phthalazine which interacts with DNA by intercalation. (1990) J. of Medical Chemistry, 34, 82-86.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00105a014
Casasnovas JM, Ellison MJ, Rodríguez-Campos A, Martínez-Balbás MA, Azorín F. In vivo assesment of the Z-DNA forming potenetial of (CG)n and (CA)n sequences cloned into SV40 minichromosomes. (1989) J. Mol. Biol, 208, 537-549.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(89)90146-0
Project funding
RESEARCH GRANTS
Investigando el papel de las desmetilasas de histonas phf2 y jmjd3 proporcionando información transcripcional, metabólica y estructural en células madre neurales. PID2021-125862NB-I00
- Spanish Ministry for Science and Innovation
- From: 01/09/2022 Duration: 3 years
- Principal Investigator: Marian Martínez-Balbás
Proyecto PID2021-125862NB-I00 financiado por:

Chromatin activity and homeostasis in neural stem cells: characterization of the role histone demethylases PHF2 and JMJD3. PGC2018-096082-B-I00
- Spanish Ministry for Science and Innovation
- From: 01/01/2019 To: 31/12/2021
- Principal Investigator: Marian Martínez-Balbás
Impact of the histone demethylases JMJD3 and PHF8 in the function of neural stem cells, early neurogenesis and their implications in intellectual disability. BFU2015-69248
- Spanish Ministry for Science and Innovation
- From: 01/01/2016 To: 31/12/2018
- Principal Investigator: Marian Martínez-Balbás
Proyecto BFU2015-69248 financiado por:

Vacancies/Jobs
PREDOCTORAL POSITION IN EPIGENETICS
PREDOCTORAL POSITION IN EPIGENETICS A predoctoral position is available to work on epigenetics and neurogenesis.…
OFERTA DE CONTRATO PREDOCTORAL
OFERTA DE CONTRATO PREDOCTORAL Se ofrece contrato predoctoral para trabajar en el Instituto de Biología…