Lab presentation
The aim of this subline is to understand the process of signal transduction that let to changes in cell structure and function in physiology and diseases. We focus our attention on G proteins that are molecular switches that signal through their receptors, GPCRs, at the plasma membrane.
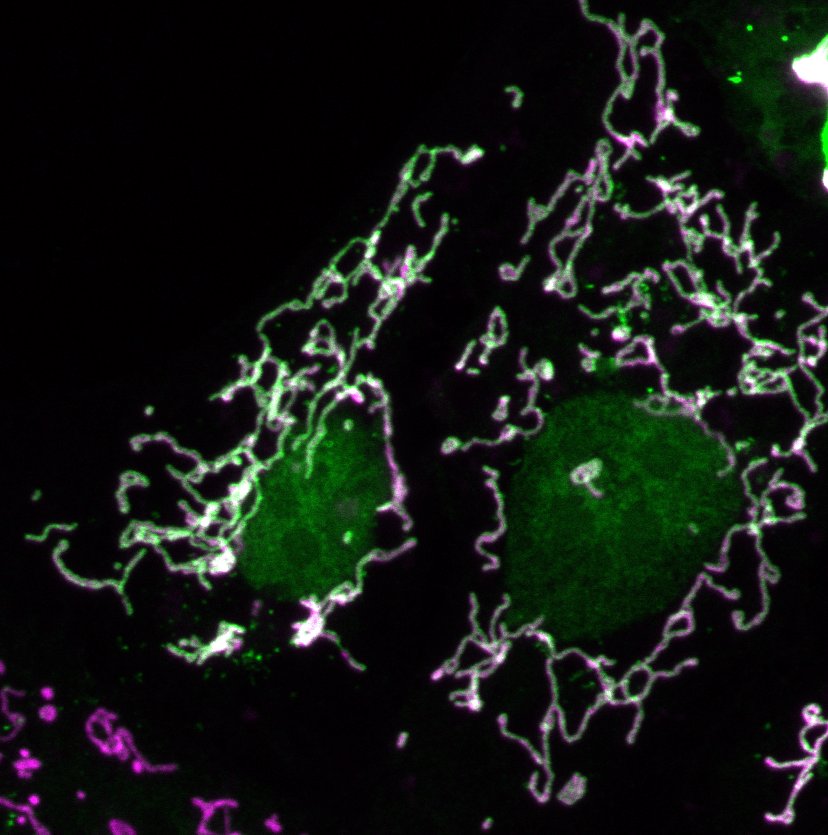
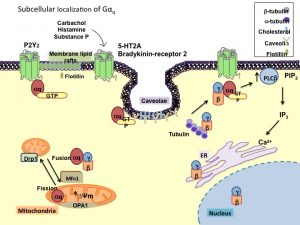
However, a novel localization of G proteins at the mitochondria and other endomembranes where they regulate the physiology of these organelles has been recently demonstrated by our group. We focus our attention in understanding how the G proteins control the proper balance between mitochondria fusion and fission, their dynamic movement and the mitochondrial physiology.
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles that produce most of the energy of the cell. Broken mitochondria cristae, and loss of internal structure impairs many of the functions of mitochondria and its present in neurons of several neurodegenerative diseases.
In order to unveil the putative effectors of G proteins that mediate those effects at the mitochondria, our group has undertaken a mass-spectrometry analysis based on G protein-immunoprecipitates from cellular endomembranes using different cell lines: “mito-intereactome”.
In addition, our projects relay heavily on the use of “state of the art” imaging technologies that helps us to answer crucial questions on mitochondria dynamics and neuronal physiology.
Projects
Research lines
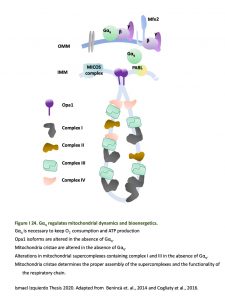
GPCRs, G proteins and their signaling pathways are linked to a myriad of physiological processes and to the prognosis of numerous human diseases including cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Although signaling pathways are important in the control cellular homeostasis, until recently, not much was known about the G protein signaling effects on the mitochondria. However, there is an emerging evidence of their presence inside the cell. Our group demonstrated the localization of Gαq subunit at the mitochondria membrane that affects mitochondrial morphology and is required for OXPHOS function. Through a proteome-wide approach we identified mitochondrial partners for Gq. This analysis identified a group of proteins involved in the process of mitophagy and others in control of the mitochondria motility, among others.
Project I. G protein regulation of mitochondrial dynamics.
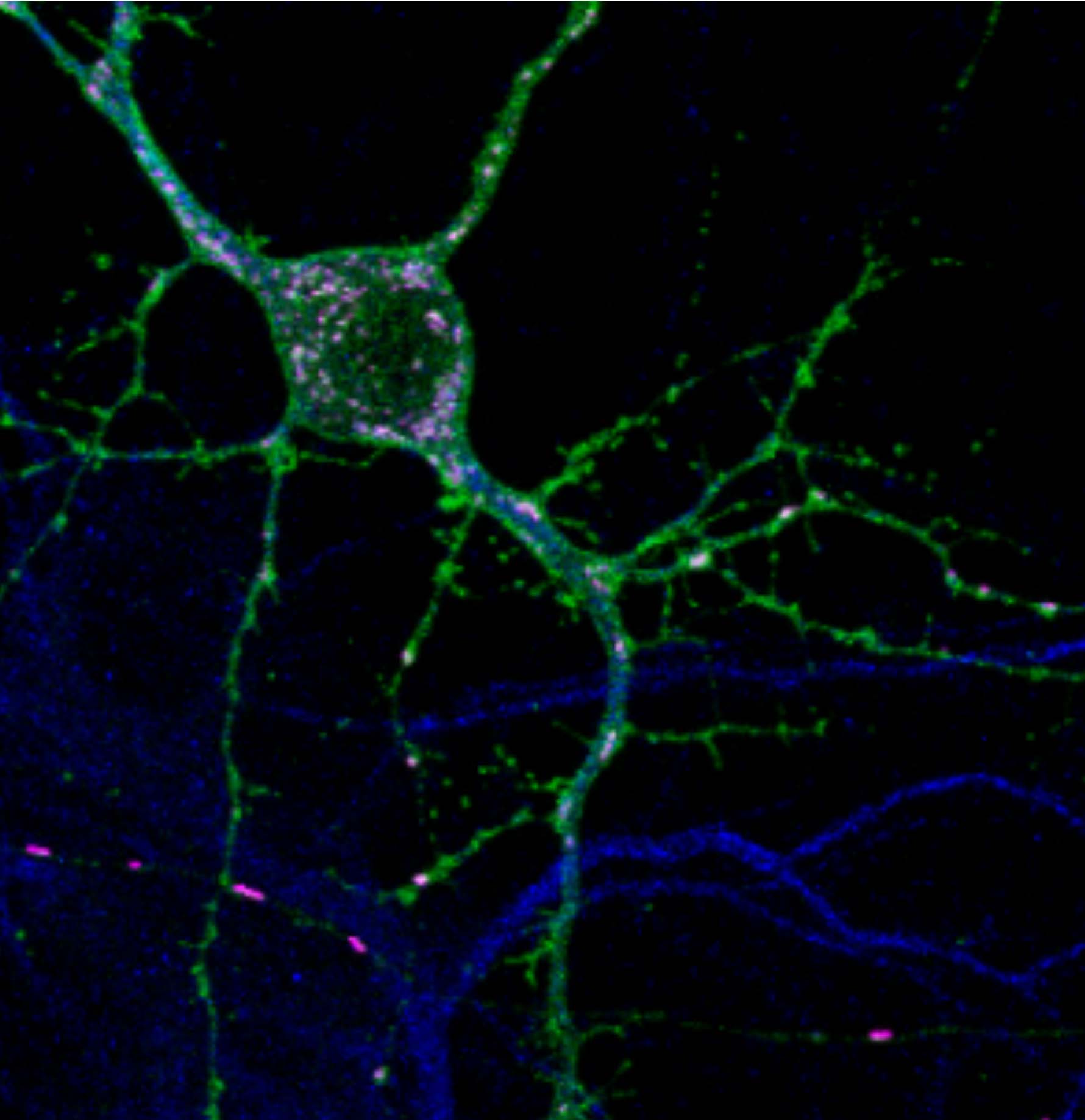
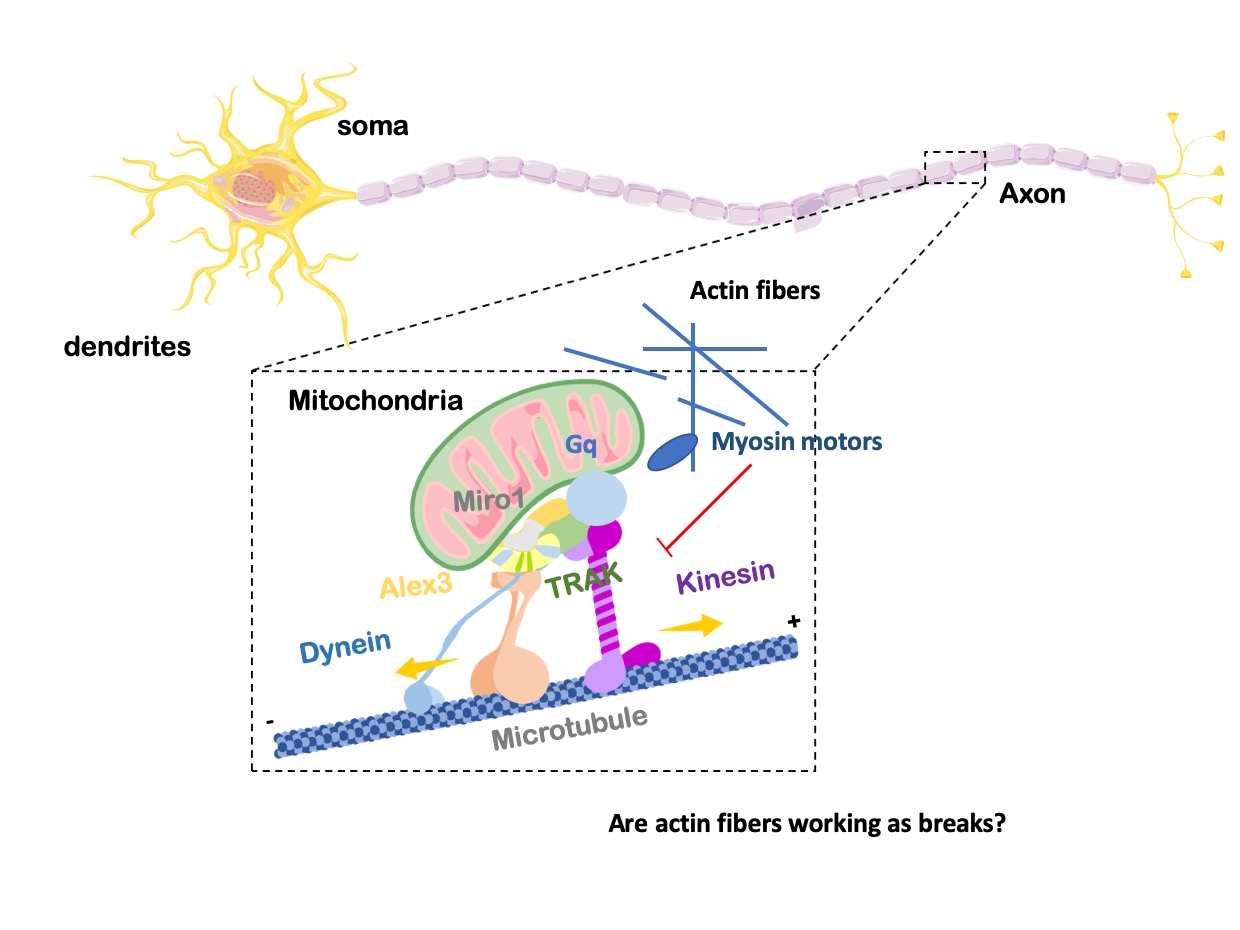
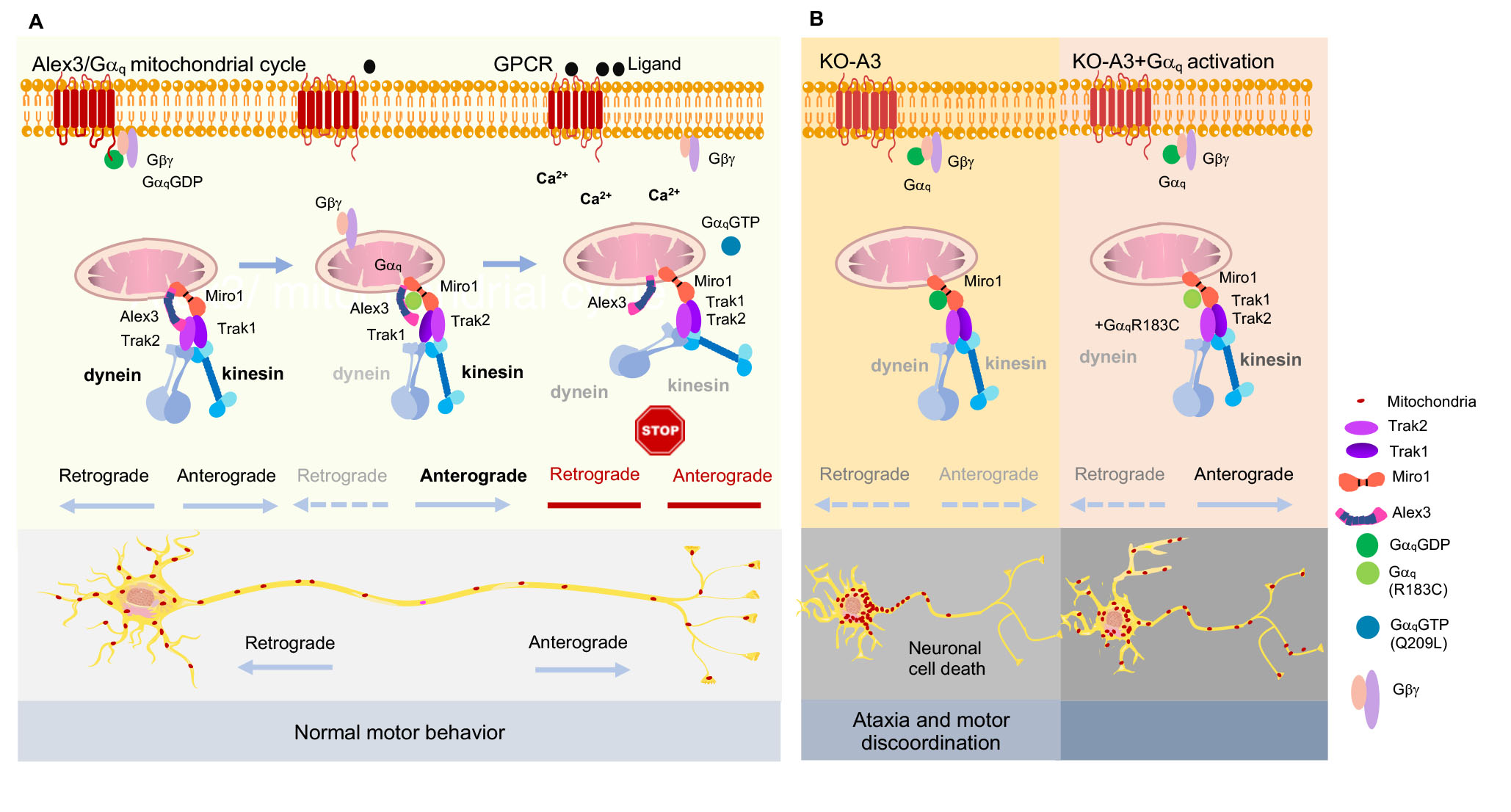
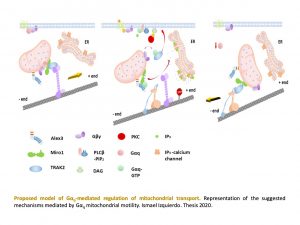
Our studies have demonstrated that the mitochondrial trafficking protein, armadillo-domain protein (Alex3), directly interacts with Gq and acts as an activator independent of Gbg and GPCRs. Alex protein is a member of the Eutherian-specific Armcx gene family localized to the mitochondria. Alex3 is preferentially expressed in the upper layers of the developing cerebral cortex. Life-cell imaging of mitochondria revealed that Gaq is needed for the regulation of the anterograde and retrograde movement of mitochondria along the axons of hippocampal neurons. Utilizing knockout and knockdown techniques, we demonstrated that Alex3 is required for Gaq effects on mitochondrial trafficking and dendritic growth. These proteins control mitochondrial distribution and trafficking, dendritic complexity, synapse formation and neuronal survival.
How does Gq regulate mitochondria speed?
In our previous results, we found an increase in overall mitochondrial speed in the absence of Gaq. This cannot be accounted for by microtubule coupling or Alex3 interaction and requires the involvement of side-mechanisms that modulate motility. Thus, Gaq signaling could be regulating the coupling of mitochondria to actin filaments through the actin modulators like myosins, as has been proposed for transport in dendritic spines and synaptic buttons, and interaction with Miro1. Similarly, the increase in mitochondrial length observed in neurons with low levels of Gaq could be linked to myosin regulation. This project investigates whether myosins could be the missing piece to support the movement of mitochondria controlled by Gq proteins along the microtubules under the control of small patches of actin.
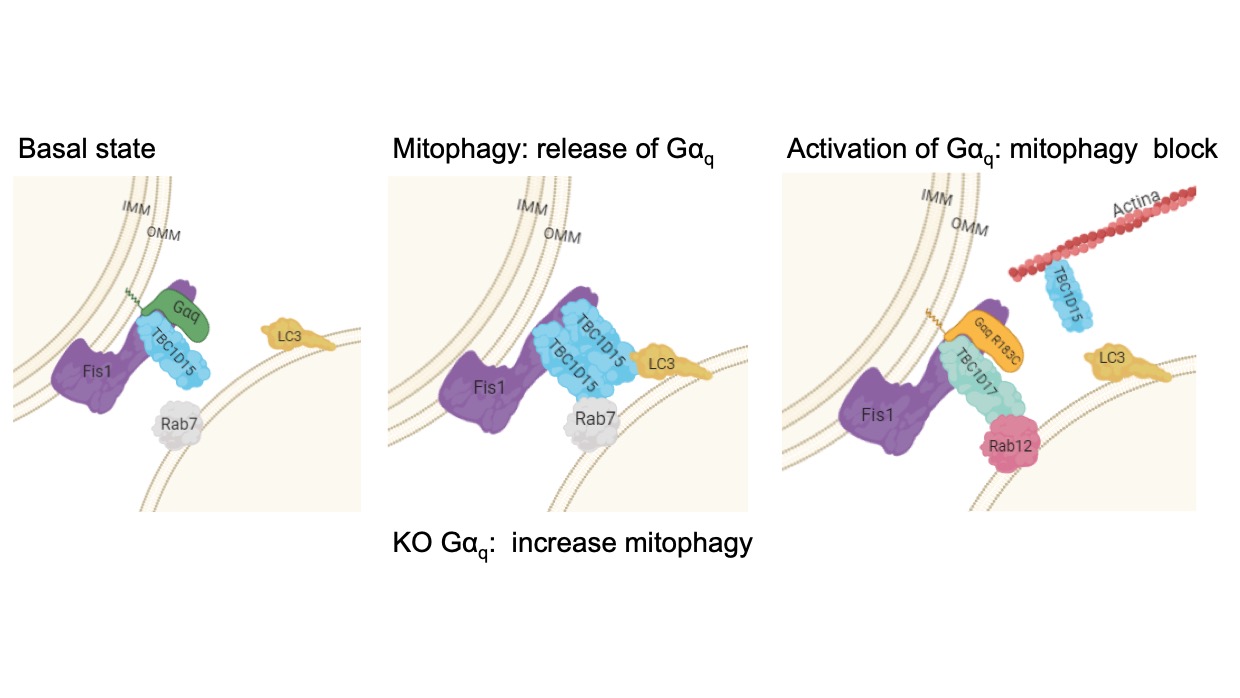
Project II. Gq regulates mitophagy.
In order to prevent the expansion of damage through the mitochondrial network, damaged mitochondria are depleted through specialized form of autophagy, mitophagy. Perturbed mitophagy was found to be involved in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimers or Parkinsons disease, and other various age-dependent diseases. The results from the group have demonstrated that Gq is necessary for mitophagy during the process of autosomal maturation. Gq forms a ternary complex with the mitochondrial protein Fis1 and the Rab7GAP protein TBC1D15.
How does Gq control the traffic of Rab7 vesicles?
Rab7 utilizes its effector RILP to recruit the dynein motor to head to lysosome for degradation. Contrary to RILP, SKIP is recruited to Rab7 to engage kinesin-1 to transport vesicles to periphery. Recent results have demonstrated that the switch involves recruitment of TBC1D15 to SKIP to remove Rab7. This project analyzes how Gq controls the traffic of autolysosomal vesicles through TBC1D15 and its effect on the recruitment of Rab7 vesicles.
Lab people

Anna Aragay
Principal investigator
Anna M. Aragay is the head of the “Signaling Transduction group” at IBMB-CSIC. She obtained her PhD. at the Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB) in 1989. In 1990 she moved to the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) at USA for a postdoct with Prof. M. Simon where she focus her interest in signal transduction processes.
During this period she had a close collaboration with Prof. H. Brown at UCSD where she implemented microinjecting techniques for signal inhibition and with Prof. H. Lester at Caltech using electrophysiology for GPCR studies. In 1996, she joint the group of Prof. F. Mayor at CBM, Madrid, as a junior scientist, studying chemokine signaling.
As Associated Professor at the University of Bergen (UiB), Norway, she established her research group in 1999 and became Professor in 2005. For four years she directed the Norwegian National platform for Molecular Imaging (MIC). In mid-2006, she became “Científico titular” at IBMB where she established-back her actual group.

Monica Pons

Miriam Ferrando
Past students
Alicia Josa
Ismael Izquierdo Villalba
Mireia Andreu
Georgina Garrido
Míriam Masià
Cristiane Beninca
Laura Minsaas
Vandana Ardawatia
Beate Fast
Javier Rubio Contijoch
Noura Abdala
Diego Martín Garcia
Maria Gomez
Fatime Zara
Amitie Aminian
Selected publications
Kazrin promotes dynein/dynactin-dependent traffic from early to recycling endosomes
I Hernandez-Perez, J Rubio, A Baumann, H Girao, M Ferrando, E Rebollo, …
2023 Elife 12, e83793. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83793
Gq signaling in autophagy control: between chemical and mechanical cues
I Navarro-Lérida, AM Aragay, A Asensio, C Ribas
2022 Antioxidants 11 (8), 1599. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081599
Izquierdo-Villalba,I, Mirra, S,, Manso, Y, Parcerisas,A, Rubio, J, Del Valle, J, Gil-Bea, FJ, Ulloa, F, Herrero-Lorenzo, M, Verdaguer, E, Benincá, C, Castro-Torres, RD, Rebollo,, E, Marfany, G, Auladell, C, Navarro, X, Enríquez, JA, López de Munain, L, Soriano, E and AM Aragay. «A mammalian-specific Alex3/Gαq protein complex regulates mitochondrial trafficking, dendritic complexity, and neuronal survival». Science Signaling, Feb 6 2024, 17, 822. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abq1007
Cabezudo S, Sanz-Flores M, Caballero A, Tasset I, Rebollo E, Diaz A, Aragay AM, Cuervo AM, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. (2021). Gαq activation modulates autophagy by promoting mTORC1 signaling. Nature Communications. 2021 Jul 27;12(1):4540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24811-4
Selheim F, Aasebø E, Ribas C, Aragay AM. (2019). An overview on G protein-coupled receptor-induced signal transduction in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2019 Apr 29. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190429153247
Pons M, Izquierdo I, Andreu-Carbó M, Garrido G, Planagumà J, Muriel O, Geli MI, Aragay AM. (2017). Phosphorylation of filamin A regulates chemokine receptor CCR2 recycling. Journal of Cell Science. 2017 Jan 15. doi: 10.1242/jcs.193821
Masià-Balagué M, Izquierdo I, Garrido G, Cordomí A, Pérez-Benito L, Miller NL, Schlaepfer DD, Gigoux V, Aragay AM. (2015). Gastrin-stimulated Gα13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15197-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628164
Benincá C, Planagumà J, de Freitas Shuck A, Acín-Perez R, Muñoz JP, de Almeida MM, Brown JH, Murphy AN, Zorzano A, Enríquez JA, Aragay AM. (2014). A new non-canonical pathway of Ga(q) protein regulating mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics. Cellular Signalling. 2014 26:1135-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.009
Sánchez-Fernández G, Cabezudo S, García-Hoz C, Benincá C, Aragay AM, Mayor F Jr, Ribas Filamin C. (2014). Gaq signalling: the new and the old. Cellular Signalling. 2014 26:833-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.010
Nygaard G, Herfindal L, Kopperud R, Aragay AM, Holmsen H, Døskeland SO, Kleppe R, Selheim F. (2014). Time-dependent inhibitory effects of cGMP-analogues in thrombin-induced platelet-derived microparticles formation, platelet aggregation, and P-selectin expression. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2014 Jul 4;449(3):357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.032
Planagumà J, Minsaas L, Pons M, Myhren L, Garrido G, Aragay AM. (2012). A-hinge region1-EGFP: a novel tool for tracking the cellular functions of Filamin A in real-time. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e40864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040864
Minsaas L, Planagumà J, Madziva M, Krakstad BF, Masià-Balagué M, Katz AA, Aragay AM. (2010). Filamin a binds to CCR2B and regulates its internalization. PLoS One 5(8):e12212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012212
Jiménez-Sainz, MC., Murga, C., Kavelaars, A. , Jurado, M., Fast-Kraastak, B., Heijnen, C.J. Mayor, F. and Aragay, A. M. (2006). G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 2 Negatively Regulates Chemokine Signaling at a Level Downstream from G Protein Subunits at a level downstream from G protein subunits. Molecular Biology of the Cell 17(1):25-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-05-0399
B.B. Johannson, Minsaas L. & Aragay, A.M. (2005). Proteasome involvement in the degradation of the Gq family of Gα subunits. The FEBS Journal 272(20), 5365-5377. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04934.x
Krastad, B., V. Ardavatia & Aragay, AM. (2004). A role for Ga12/Ga13 in p120ctn regulation. PNAS, 101(28), 10314-10319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401366101
M.C. Jimenez, Fast, B, Mayor, F., jr. & A.M.Aragay (2003). Signaling Pathways for Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1-Mediated Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Activation. Molecular Pharmacology 64, 773-782. doi: 10.1124/mol.64.3.773
All publications
Kazrin promotes dynein/dynactin-dependent traffic from early to recycling endosomes
I Hernandez-Perez, J Rubio, A Baumann, H Girao, M Ferrando, E Rebollo, …
2023 Elife 12, e83793. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83793
Gq signaling in autophagy control: between chemical and mechanical cues
I Navarro-Lérida, AM Aragay, A Asensio, C Ribas
2022 Antioxidants 11 (8), 1599. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081599
Izquierdo-Villalba,I, Mirra, S,, Manso, Y, Parcerisas,A, Rubio, J, Del Valle, J, Gil-Bea, FJ, Ulloa, F, Herrero-Lorenzo, M, Verdaguer, E, Benincá, C, Castro-Torres, RD, Rebollo,, E, Marfany, G, Auladell, C, Navarro, X, Enríquez, JA, López de Munain, L, Soriano, E and AM Aragay. «A mammalian-specific Alex3/Gαq protein complex regulates mitochondrial trafficking, dendritic complexity, and neuronal survival». Science Signaling, Feb 6 2024, 17, 822. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abq1007
Kazrin C entraps early endosomes at the pericentriolar region and facilitates endocytic recycling | Hernandez-Perez, A Baumann, H Girao, AM Aragay… – bioRxiv, 2021. doi: 10.1101/2021.08.30.458243
A novel Alex3/Gαq protein complex regulating mitochondrial dynamics, dendritic complexity, and neuronal survival | Izquierdo-Vallalba, S Mirra, Y Manso, A Parcerisas… – bioRxiv, 2021. doi: 10.1101/2021.12.09.471902
Cabezudo S, Sanz-Flores M, Caballero A, Tasset I, Rebollo E, Diaz A, Aragay AM, Cuervo AM, Mayor F Jr, Ribas C. (2021). Gαq activation modulates autophagy by promoting mTORC1 signaling. Nature Communications. 2021 Jul 27;12(1):4540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24811-4
An overview on G protein-coupled receptor-induced signal transduction in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Selheim F, Aasebø E, Ribas C, Aragay AM.. Current Medicinal Chemistry 2019 Apr 29. 26(28):5293-5316. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190429153247
Phosphorylation of Filamin A regulates chemokine receptor CCR2 recycling. Pons M, Izquierdo I, Andreu-Carbó M, Garrido G, Planagumà J, Muriel O, Geli MI, Aragay AM. Journal of Cell Science. 2017 Jan 15;130(2):490-501. doi: 10.1242/jcs.193821
Gastrin-stimulated Gα13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells. Masià-Balagué M, Izquierdo I, Garrido G, Cordomí A, Pérez-Benito L, Miller NL, Schlaepfer DD, Gigoux V, Aragay AM. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15197-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628164
A new non-canonical pathway of Gα(q) protein regulating mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics. Benincá C, Planagumà J, de Freitas Shuck A, Acín-Perez R, Muñoz JP, de Almeida MM, Brown JH, Murphy AN, Zorzano A, Enríquez JA, Aragay AM. Cellular Signaling. 2014 26:1135-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.009
Gαq signalling: the new and the old. Sánchez-Fenández G, Cabezudo S, García-Hoz C, Benincá C, Aragay AM, Mayor F Jr, Ribas. Cellular Signaling. 2014 26:833-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.010
Time-dependent inhibitory effects of cGMP-analogues in thrombin-induced platelet-derived microparticles formation, platelet aggregation, and P-selectin expression. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. Nygaard G, Herfindal L, Kopperud R, Aragay AM, Holmsen H, Døskeland SO, Kleppe R, Selheim F. 2014 Jul 4;449(3):357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.032
A-hinge region1-EGFP: a novel tool for tracking the cellular functions of Filamin A in real-time. Planagumà J, Minsaas L, Pons M, Myhren L, Garrido G, Aragay AM.. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e40864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040864
Gα(12) binds to the N-terminal regulatory domain of p120(ctn), and downregulates p120(ctn) tyrosine phsophorylation induced by Src family kinases via a RhoA indepnedent mechanism. Ardawatia VV, Masià-Balagué M, Krakstad BF, Johansson BB, Kreitzburg KM, Spriet E, Lewis AE, Meigs TE, Aragay AM. Experimental Cell Research 2011 Feb 1;317(3):293-306. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.10.017
Filamin a binds to CCR2B and regulates its internalization. Minsaas L, Planagumà J, Madziva M, Krakstad BF, Masià-Balagué M, Katz AA, Aragay AM. PLoS One 2010 5(8):e12212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012212
GRK2 negatively regulates chemokine activation of ERK cascade at a level downstream from G protein subunits. Jiménez-Sainz, MC., Murga, C., Kavelaars, A. , Jurado, M., Fast-Kraastak, B., Heijnen, C.J. Mayor, F., Aragay, A. M. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2006 Jan;17(1):25-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-05-0399
Proteosome involvement in Galphaq and Galpha16 protein degradation. B.B. Johannson, Minsaas L. & Aragay, A.M. The FEBS Journal. 2005. 272, 5365-5377. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04934.x
A role for Ga12/Ga13 in p120ctn regulation. Krastad, B., V. Ardavatia & Aragay, AM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2004 101, 10314-10319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401366101
Signaling Pathways for Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1-Mediated Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Activation. M.C. Jimenez, Fast, B, Mayor, F., jr. & A.M.Aragay Molecular Pharmacology. 2003. 64, 773-782. doi: 10.1124/mol.64.3.773
Functional regulation of Galpha16 by protein Kinase C. Aragay AM, Quick MW. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999 19;274(8):4807-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.8.4807
G protein-coupled receptro kinase 2 (GRK2): mechanisms of regulation and physiologycal functions. Aragay AM, Ruiz-Gómez A, Penela P, Sarnago S, Elorza A, Jiménez-Sainz MC, Mayor F Jr. FEBS Letters. 1998 Jun 23;430(1-2):37-40. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00495-5
The chemokine monocyte chemoatactic protein 1 triggers Janus kinase 2 activation and tyrosine phsophorylation of the CCR2B receptor. Mellado M, Rodríguez-Frade JM, Aragay A, del Real G, Martín AM, Vila-Coro AJ, Serrano A, Mayor F Jr, Martínez-A C. The Journal of Immunology. 1998 Jul 15;161(2):805-13. https://www.jimmunol.org/content/161/2/805
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-induced CCR2B receptor desensitization mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Aragay AM, Mellado M, Frade JM, Martin AM, Jimenez-Sainz MC, Martinez-A C, Mayor F Jr. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 11998 Mar 17;95(6):2985-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.2985
Desensitization of inositol 1,4,5-triphsopate/Ca2+-induced Cl- currents by prolonged activation of G proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Quick MW, Lester HA, Davidson N, Simon MI, Aragay AM. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996 Dec 13;271(50):32021-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.32021
A novel form of the Gbeta5 is specifically expressed in the vertebrate retina. Watson AJ, Aragay AM, Slepak VZ, Simon MI. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996 Nov 8;271(45):28154-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.45.28154
Coupling of the thrombin receptor to G12 may account for the selective effects of thrombin on gene expression and DNA systhesis in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Post GR, Collins LR, Kennedy ED, Moskowitz SA, Aragay AM, Goldstein D, Brown JH. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 1996 Nov;7(11):1679-90. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.11.1679
Cell-specific signal transduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH)-related protein through stabley expressed recombinant PTH/PTHrP receptros in vacular smooth muscle cells. Maeda S, Wu S, Jüppner H, Green J, Aragay AM, Fagin JA, Clemens TL. Endocrinology. 1996 Aug;137(8):3154-62. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.8.8754733
Increase expression of alphaq family G-proteins during oocyte maturation and early development of Xenopus laevis. Gallo CJ, Jones TL, Aragay AM, Jaffe LA. Developmental Biology. 1996 Jul 10;177(1):300-8. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0164
G12 requirement for thrombin-stimulated gene exoression and DNA synthesis in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Aragay AM, Collins LR, Post GR, Watson AJ, Feramisco JR, Brown JH, Simon MI. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995 Aug 25;270(34):20073-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.20073
Differential coupling of G protein alpha subunits to seven-helix receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Quick MW, Simon MI, Davidson N, Lester HA, Aragay AM. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30164-72. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)43792-1
Design of degenerate oligonucleotide primers for cloning of G-protein alpha subunits. Wilkie TM, Aragay AM, Watson AJ, Simon MI. Methods in Enzymology. 1994;237:327-44. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(94)37073-7
Random mutagenesis of G protein alpha subunits G(o)alpha. Mutations alterin nucleotide binding. Slepak VZ, Quick MW, Aragay AM, Davidson N, Lester HA, Simon MI. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21889-94. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(20)80624-3
The G alpha q and G alpha 11 proteins couple the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C in GH3 rat pituitary cells. Aragay AM, Katz A, Simon MI. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24983-8. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)73994-5
Project funding

Estudio del mitointeratoma de Gq en las neuronas
- Financiado por: MINECO BFU2017-83379-R
- Duración: 2018-2020
- Investigador Principal: A.M. Aragay
Proyecto BFU2017-83379-R financiado por:

Gq: de la mitocondria a los cardiomiocitos
- Financiado por: MINECO BFU2014-53978-R
- Duración: 2015-2017
- Investigador Principal: A.M. Aragay
Procesos de señalización por proteínas G implicados en migración celular
- Financiado por: MINECO BFU2011-30080
- Duración: 2012-2014
- Investigador Principal: A.M. Aragay
Estudio de la interacción de la proteína G12 con p120 catenina
- Financiado por: MINISTERIO DE CIENCIA E INNOVACION BFU2008-04262
- Duración: 2009-2011
- Investigador Principal: A. M. Aragay
Mecanisme i funció del tràfic endocític
- Financiado por: AGAUR SRG 41635 Grupo de Investigación emergente.
- Duración: 2009-2014
MAGING G PROTEINS IN CELL ADHESION AND MIGRATION
- Financiado por: HELSE VEST 12458 NORWAY
- Duración: 2008-2010
- Investigador Principal: A. M. Aragay
Vacancies/Jobs
The group is seeking students to perform experimental research projects for TFG, Master or PhD.
The students will be participating in the ongoing research of the group and will utilize a variety of techniques ranging from cell culture (transfection, shRNA, handling of primary neonatal cardiomyocytes), molecular biology (PCR cloning, mutagenesis) and immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy, among others.
The Signal Transduction group tackle research projects bridging the gap from molecular mechanisms of cellular biology to physiology and pathologies. Our group has directed more than 32 research projects among TFG, TFM and Thesis. All of them obtained excellent evaluations of their projects.
If you feel passionate about research and have excellent academic records, this opportunity will open up your eyes to the world of research.