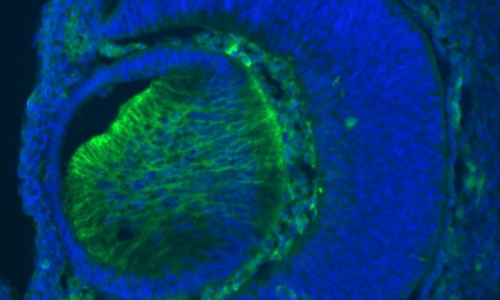
Lab presentation
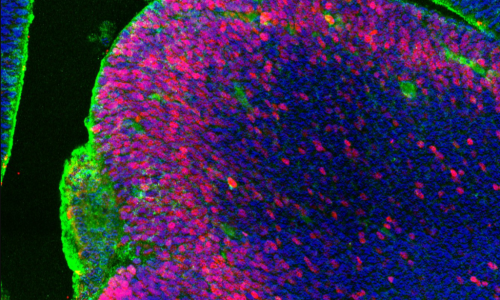
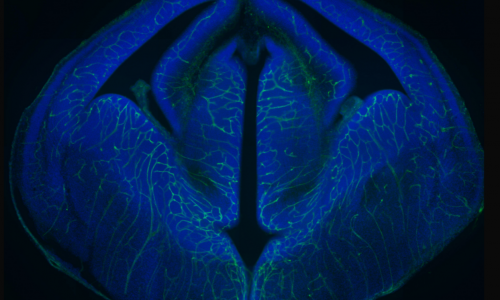
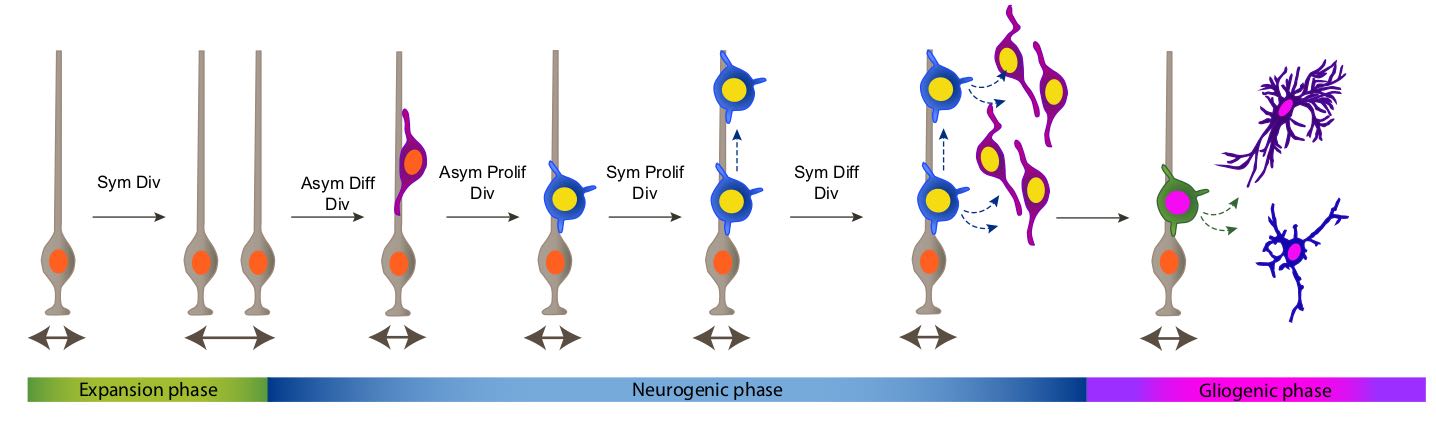
The cerebral cortex is the most evolved region of the human brain and responsible for higher cognitive functions and sophisticated behaviors. Cortical circuits are formed by an enormous number of specialized subtypes of neurons that are morphologically and functionally very heterogeneous. These neurons are generated during embryonic development and can be divided in two main groups: excitatory neurons that extend long axons and target cortical areas as well as other regions and inhibitory neurons, which are less abundant and make local connections to ensure that excitation remains in check. All these neurons are produced in a stereotyped manner from progenitors located in different germinal domains of the telencephalon. Shortly after mitosis, new-born neurons migrate from these domains to the future neocortex where they mature and ensemble into circuits. Alterations in cortical neuron production might result in aberrant brain structures and architectures or in more subtle defects affecting cortical subnetworks that may still cause major brain dysfunctions.
In the laboratory we use the mouse to study the mechanisms that regulate organ growth and cell diversity in the mammalian central nervous system. We are particularly interested in the development of cortical projection neurons in healthy and pathological brains. We want to know how the progenitors that produce these neurons sense environmental signals to balance proliferation and differentiation and how alterations in this balance impact on the developmental outputs.
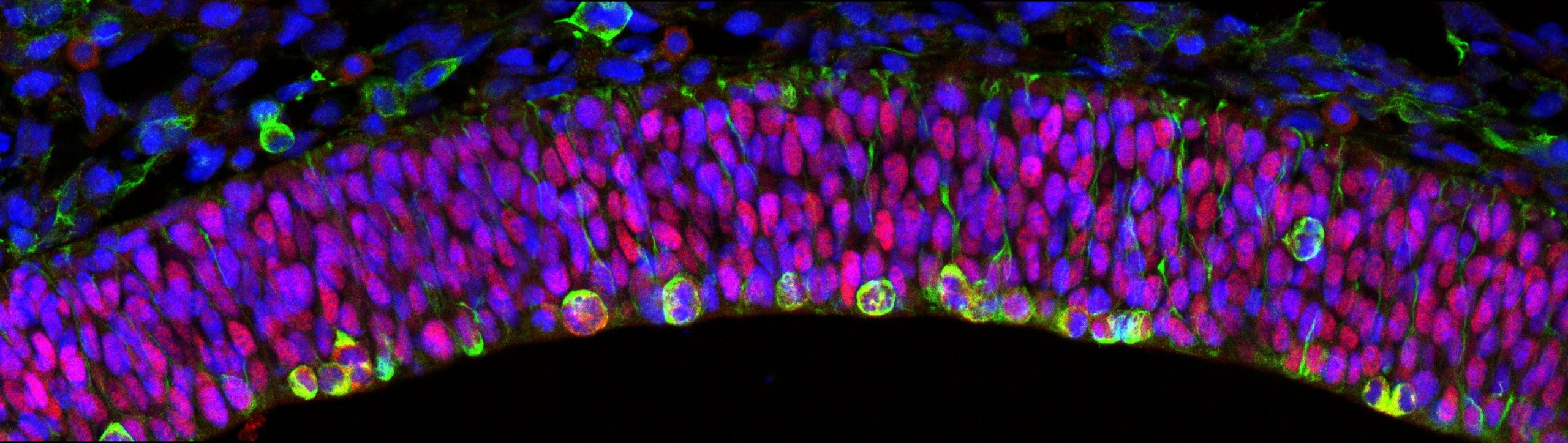
Projects
Role of kinase DYRK1A in cortical development
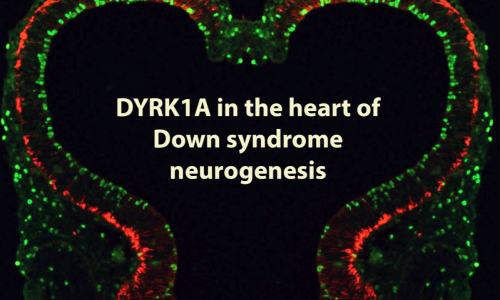
DYRK1A is a member of the evolutionary conserved dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase (DYRK) family of protein kinases. This kinase has many putative substrates related to a variety of functions including transcription, DNA-repair, apoptosis, cell signalling regulation and cytoskeleton dynamics. In the developing central nervous system DYRK1A regulates neuronal proliferation, dendritogenesis and programmed cell death. DYRK1A is encoded on chromosome 21 and its overexpression contributes to the neuropathology associated with Down syndrome. Moreover, loss-of-function mutations in the DYRK1A gene cause a well-defined syndromic form of intellectual disability and autisms. Characteristic features of the DYRK1A syndrome include general developmental delay, microcephaly, impaired communicative language, moderate to severe intellectual disability, autism or autistic-like behaviours and epilepsy.
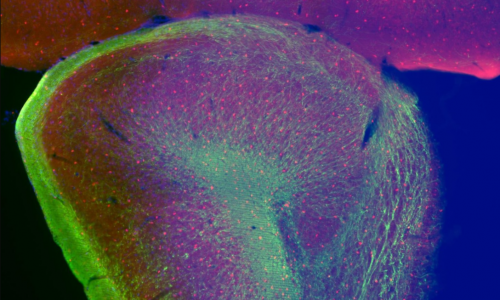
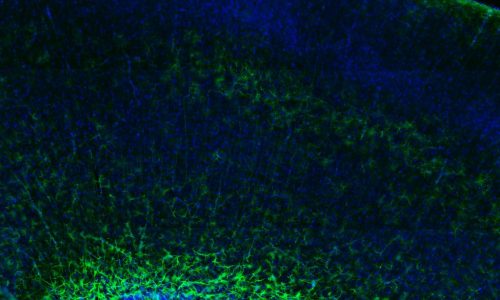
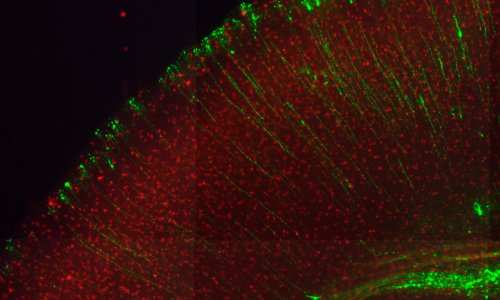
Using gain- and loss-off function Dyrk1a mouse models our laboratory has contributed to the identification of neurodevelopmental dysfunctions associated with Down syndrome and DYRK1A syndrome. In the developing neocortex, variations in the dosage of DYRK1A alter the balance between proliferative and differentiative radial glia self-renewal divisions, a defect that correlates with different neuronal outputs in all cortical layers.
Current research aims to: 1) uncover the cellular functions and activities by which DYRK1A regulates the lateral and radial expansion of the neocortex, 2) have a better understanding of the formation and maturation of cortical circuits in DYRK1A haploinsufficiency syndrome and 3) study the impact of pathogenic DYRK1A mutations on the neurogenic phase of human cortical development.
The research involves classical morphological analysis of the developing neocortex of different mouse models with one or two Dyrk1a mutant alleles, transcriptome-proteome and phospho-proteome analysis of Dyrk1a mutant cortical progenitors and studies in human 3D brain organoids.
Lab people

Mariona Arbonés
Principal investigator
Mariona Arbonés graduated in Biological Sciences at the Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB). She obtained her PhD at the same University in 1990 for work on brain histamine receptors carried out under the supervision of Agustina García. Next, she moved to a biotech company in California (Cell Genesys, Inc.) to work on gene editing in mammalian somatic cells and leucocyte homing and inflammation. In 1994, she obtained a “reintegration” contract to join Agustina Garcia’s lab at the Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina (UAB) where she studied the role of nitric oxide in glial cells. In 1996, she moved to the Department of Molecular Genetics (IRO, Barcelona) to work with Xavier Estivill in neurosensorial deafness and Down syndrome. In 2002 she joined the Center for Genomic Regulation (CRG) as a group leader. She obtained a CSIC tenure track position in 2010 and in January 2011 her lab moved to the IBMB.
Past students
Alejandro Trujillano
Sonia Najas
Laia Caudet
Isabel Pijuan
Charles Chevillard
Selected publications
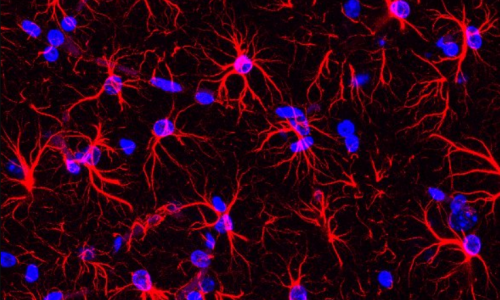
Pijuan I, Balducci E, Soto-Sánchez C, Fernández E, Barallobre MJ, Arbonés ML. Impaired macroglial development and axonal conductivity contributes to the neuropathology of DYRK1A-related intellectual disability syndrome. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 19;12(1):19912
Najas S, Pijuan I, Esteve-Codina A, Usieto S, Martinez JD, Zwijsen A, Arbonés ML, Martí E, Le Dréau G. A SMAD1/5-YAP signalling module drives radial glia self-amplification and growth of the developing cerebral cortex. Development. 2020 Jul 13;147(13):dev187005.
Arranz J, Balducci E, Arató K, Sánchez-Elexpuru G, Najas S, Parras A, RebolloE, Pijuan I, Erb I, Verde G, Sahun I, Barallobre MJ, Lucas JJ, Sánchez MP, de la Luna S, Arbonés ML. Impaired development of neocortical circuits contributes to the neurological alterations in DYRK1A haploinsufficiency syndrome. Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Jul;127:210-222.
Najas S, Arranz J, Lochhead PA, Ashford AL, Oxley D, Delabar JM, Cook SJ, Barallobre MJ, Arbonés ML. DYRK1A-mediated Cyclin D1 Degradation in Neural Stem Cells Contributes to the Neurogenic Cortical Defects in Down Syndrome. EBioMedicine. 2015 Jan 17;2(2):120-34.
Barallobre MJ, Perier C, Bové J, Laguna A, Delabar JM, Vila M, Arbonés ML. DYRK1A promotes dopaminergic neuron survival in the developing brain and in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jun 12;5(6):e1289.
Laguna A, Barallobre MJ, Marchena MÁ, Mateus C, Ramírez E, Martínez-Cue C, Delabar JM, Castelo-Branco M, de la Villa P, Arbonés ML. Triplication of DYRK1A causes retinal structural and functional alterations in Down syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Jul 15;22(14):2775-84.
Guedj F, Pereira PL, Najas S, Barallobre MJ, Chabert C, Souchet B, Sebrie C, Verney C, Herault Y, Arbones M, Delabar JM. DYRK1A: a master regulatory protein controlling brain growth. Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Apr;46(1):190-203.
Aug;47(2):294. PMID: 22293606. da Costa Martins PA, Salic K, Gladka MM, Armand AS, Leptidis S, el Azzouzi H, Hansen A, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Bierhuizen MF, van der Nagel R, van Kuik J, de Weger R, de Bruin A, Condorelli G, Arbones ML, Eschenhagen T, De Windt LJ. MicroRNA-199b targets the nuclear kinase Dyrk1a in an auto-amplification loop promoting calcineurin/NFAT signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;12(12):1220-7.
Ferron SR, Pozo N, Laguna A, Aranda S, Porlan E, Moreno M, Fillat C, de la Luna S, Sánchez P, Arbonés ML, Fariñas I. Regulated segregation of kinase Dyrk1A during asymmetric neural stem cell division is critical for EGFR-mediated biased signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Sep 3;7(3):367-79.
Arqué G, de Lagrán MM, Arbonés ML, Dierssen M. Age-associated motor and visuo-spatial learning phenotype in Dyrk1A heterozygous mutant mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2009 Nov;36(2):312-9.
Laguna A, Aranda S, Barallobre MJ, Barhoum R, Fernández E, Fotaki V, Delabar JM, de la Luna S, de la Villa P, Arbonés ML. The protein kinase DYRK1A regulates caspase-9-mediated apoptosis during retina development. Dev Cell. 2008 Dec;15(6):841-53.
Fotaki V, Dierssen M, Alcántara S, Martínez S, Martí E, Casas C, Visa J, Soriano E, Estivill X, Arbonés ML. Dyrk1A haploinsufficiency affects viability and causes developmental delay and abnormal brain morphology in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;22(18):6636-47
All publications
Publications since 2010
Pijuan I, Balducci E, Soto-Sánchez C, Fernández E, Barallobre MJ, Arbonés ML. Impaired macroglial development and axonal conductivity contributes to the neuropathology of DYRK1A-related intellectual disability syndrome. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 19;12(1):19912
Najas S, Pijuan I, Esteve-Codina A, Usieto S, Martinez JD, Zwijsen A, Arbonés ML, Martí E, Le Dréau G. A SMAD1/5-YAP signalling module drives radial glia self-amplification and growth of the developing cerebral cortex. Development. 2020 Jul 13;147(13):dev187005.
Rebollo E, Boix-Fabrés J, Arbones ML. Automated macro approach to quantify synapse density in 2D confocal images from fixed immunolabeled neural tissue Sections. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2040:71-97.
Luna J, Boni J, Cuatrecasas M, Bofill-De Ros X, Núñez-Manchón E, Gironella M, Vaquero EC, Arbones ML, de la Luna S, Fillat C. DYRK1A modulates c-MET in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to drive tumour growth. Gut. 2019 Aug;68(8):1465-1476.
Arranz J, Balducci E, Arató K, Sánchez-Elexpuru G, Najas S, Parras A, Rebollo E, Pijuan I, Erb I, Verde G, Sahun I, Barallobre MJ, Lucas JJ, Sánchez MP, de la Luna S, Arbonés ML. Impaired development of neocortical circuits contributes to the neurological alterations in DYRK1A haploinsufficiency syndrome. Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Jul;127:210-222.
Arbones ML, Thomazeau A, Nakano-Kobayashi A, Hagiwara M, Delabar JM. DYRK1A and cognition: A lifelong relationship. Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Feb;194:199-221.
Latour A, Gu Y, Kassis N, Daubigney F, Colin C, Gausserès B, Middendorp S, Paul JL, Hindié V, Rain JC, Delabar JM, Yu E, Arbones M, Mallat M, Janel N. LPS-induced inflammation abolishes the effect of DYRK1A on IkB stability in the brain of mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Feb; 56(2):963-975.
Rozen EJ, Roewenstrunk J, Barallobre MJ, Di Vona C, Jung C, Figueiredo AF, Luna J, Fillat C, Arbonés ML, Graupera M, Valverde MA, de la Luna S. DYRK1A kinase positively regulates angiogenic responses in endothelial cells. Cell Rep. 2018 May 8;23(6):1867-1878.
Janel N, Alexopoulos P, Badel A, Lamari F, Camproux AC, Lagarde J, Simon S, Feraudet-Tarisse C, Lamourette P, Arbones M, Paul JL, Dubois B, Potier MC, Sarazin M, Delabar JM. Combined assessment of DYRK1A, BDNF and homocysteine levels as diagnostic marker for Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 20;7(6):e1154.
Najas S, Arranz J, Lochhead PA, Ashford AL, Oxley D, Delabar JM, Cook SJ, Barallobre MJ, Arbonés ML. DYRK1A-mediated Cyclin D1 Degradation in Neural Stem Cells Contributes to the Neurogenic Cortical Defects in Down Syndrome. EBioMedicine. 2015 Jan 17;2(2):120-34.
Blazek JD, Malik AM, Tischbein M, Arbones ML, Moore CS, Roper RJ. Abnormal mineralization of the Ts65Dn Down syndrome mouse appendicular skeleton begins during embryonic development in a Dyrk1a-independent manner. Mech Dev. 2015 May; 136:133-42.
Delabar JM, Latour A, Noll C, Renon M, Salameh S, Paul JL, Arbones M, Movassat J, Janel N. One-carbon cycle alterations induced by Dyrk1a dosage. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014 Nov 21;1:487-492.
García-Cerro S, Martínez P, Vidal V, Corrales A, Flórez J, Vidal R, Rueda N, Arbonés ML, Martínez-Cué C. Overexpression of Dyrk1A is implicated in several cognitive, electrophysiological and neuromorphological alterations found in a mouse model of Down syndrome. PLoS One. 2014 Sep 4;9(9):e106572.
Janel N, Sarazin M, Corlier F, Corne H, de Souza LC, Hamelin L, Aka A, Lagarde J, Blehaut H, Hindié V, Rain JC, Arbones ML, Dubois B, Potier MC, Bottlaender M, Delabar JM. Plasma DYRK1A as a novel risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Aug12;4:e425.
Barallobre MJ, Perier C, Bové J, Laguna A, Delabar JM, Vila M, Arbonés ML. DYRK1A promotes dopaminergic neuron survival in the developing brain and in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jun 12;5:e1289.
Souchet B, Guedj F, Sahún I, Duchon A, Daubigney F, Badel A, Yanagawa Y, Barallobre MJ, Dierssen M, Yu E, Herault Y, Arbones M, Janel N, Créau N, Delabar JM. Excitation/inhibition balance and learning are modified by Dyrk1a gene dosage. Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Sep;69:65-75.
Rachdi L, Kariyawasam D, Guez F, Aïello V, Arbonés ML, Janel N, Delabar JM, Polak M, Scharfmann R. Dyrk1a haploinsufficiency induces diabetes in mice through decreased pancreatic beta cell mass. Diabetologia. 2014 May;57(5):960-9
Martin KR, Layton D, Seach N, Corlett A, Barallobre MJ, Arbonés ML, Boyd RL, Scott B, Pritchard MA. Upregulation of RCAN1 causes Down syndrome-like immune dysfunction. J Med Genet. 2013 Jul;50(7):444-54.
Laguna A, Barallobre MJ, Marchena MÁ, Mateus C, Ramírez E, Martínez-Cue C, Delabar JM, Castelo-Branco M, de la Villa P, Arbonés ML. Triplication of DYRK1A causes retinal structural and functional alterations in Down syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Jul 15;22(14):2775-84.
Martin KR, Corlett A, Dubach D, Mustafa T, Coleman HA, Parkington HC, Merson TD, Bourne JA, Porta S, Arbonés ML, Finkelstein DI, Pritchard MA. Over-expression of RCAN1 causes Down syndrome-like hippocampal deficits that alter learning and memory. Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Jul 1;21(13):3025-4, 2012.
Sobrado M, Ramirez BG, Neria F, Lizasoain I, Arbones ML, Minami T, Redondo JM, Moro MA, Cano E. Regulator of calcineurin 1 (Rcan1) has a protective role in brain ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Mar 7;9:48.
Guedj F, Pereira PL, Najas S, Barallobre MJ, Chabert C, Souchet B, Sebrie C, Verney C, Herault Y, Arbones M, Delabar JM. DYRK1A: a master regulatory protein controlling brain growth. Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Apr;46(1):190-203.
Oeschger FM, Wang WZ, Lee S, García-Moreno F, Goffinet AM, Arbonés ML, Rakic S, Molnár Z. Gene expression analysis of the embryonic subplate. Cereb Cortex. 2012 Jun; 22(6):1343-59.
Esteban V, Méndez-Barbero N, Jiménez-Borreguero LJ, Roqué M, Novensá L, García-Redondo AB, Salaices M, Vila L, Arbonés ML, Campanero MR, Redondo JM. Regulator of calcineurin 1 mediates pathological vascular wall remodeling. J Exp Med. 2011 Sep 26;208(10):2125-39.
da Costa Martins PA, Salic K, Gladka MM, Armand AS, Leptidis S, el Azzouzi H, Hansen A, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Bierhuizen MF, van der Nagel R, van Kuik J, de Weger R, de Bruin A, Condorelli G, Arbones ML, Eschenhagen T, De Windt LJ. MicroRNA-199b targets the nuclear kinase Dyrk1a in an auto-amplification loop promoting calcineurin/NFAT signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;12(12):1220-7.
Ferron SR, Pozo N, Laguna A, Aranda S, Porlan E, Moreno M, Fillat C, de la Luna S, Sánchez P, Arbonés ML*, Fariñas I*. Regulated segregation of kinase Dyrk1A during asymmetric neural stem cell division is critical for EGFR-mediated biased signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2010 Sep 3;7(3):367-79.
Project funding
2022-2023
Development of human 3D organoids to understand the differential impact of DYRK1A haploinsufficiency syndrome in the CNS
Founded by the Spanish Network on Rare Diseases, CIBERER
Role: Coordinator
2020-2023
Dissecting the role of DYRK1A kinase in neurogenesis and neuron differentiation using conditional mutant mice
Founded by the Spanish Government (PID2019-105902RB-I00)
Role: PI
Proyecto PID2019-105902RB-I00 financiado por:

2020-2022
ReDevNeural 3.0: An integrative approach to understand the logic of neural development
Founded by the Spanish Government (RED2018-102553-T)
Role: PI
2017-2020
Functions of DYRK1A kinase and microRNAs in cortical neurogenesis
Founded by the Spanish Government (SAF2016-77971-R)
Role: PI
Proyecto SAF2016-77971-R financiado por:

2017-2019
Identifying new mechanisms by which DYRK1A regulates the expansion of the cerebral cortex
Founded by the Jérôme Lejeune Foundation
Role: Participant
2017-2019
ReDevNeural 2.0: An integrative approach to understand the logic of neural development
Founded by the Spanish Government (BFU2016-81887-REDT)
Role: PI
2016-2019
Pathogenic mechanisms in the intellectual disability syndrome caused by mutations in the DYRK1A gene
Founded by the Fundación Alicia Koplowitz (FAK-2016)
Role: Coordinator
2014-2016
ReDevNeural: Generating neuronal diversity
Founded by the Spanish Government (BFU2014-55738-REDT)
Role: PI
2014-2016
Study of the molecular mechanisms that regulate the development of the cerebral cortex and their implications in mental diseases
Founded by the Spanish Goverment (SAF2013-46676-P)
Role: PI
2013 –2015
Deciphering how triplication of DYRK1A impacts in early brain neurogenesis
Founded by the Jérôme Lejeune Foundation
Role: PI
2010–2014
Dissecting the functions of the Down syndrome kinase DYRK1A in the mouse cerebral cortex and midbrain dopamine neurons
Founded by the Spanish Government (SAF2010-17004) and the CSIC
Role: PI
2009-2016
Study of the neurodevelopmental processes regulated by protein kinases and their implications in chromosome 21 aneuploidies
Founded by the Catalan Government (2009 SGR 1464; 2014 SGR 674)
Role: Participant
Vacancies/Jobs
If you are interested in joining the lab as postdoc or PhD student please send us your CV and cover letter: Mariona Arbonés (marbmc@ibmb.csic.es)
Offer of a PhD contract in the Proliferation and Differentiation of the Nervous System group
We are seekingpredoctoral candidates interested in pursuing a PhD in Biomedicine or related fields to work in a collaborative project that brings together the laboratories of Mariona Arbonés at the IBMB and Susana de la Luna at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona.
Together, we aim to identify early neurodevelopmental dysfunctions in a rare human syndrome caused by an imbalanced dosage of DYRK1A.
As a PhD student in this project, you will have the opportunity to work with state-of-the-art methodologies, including mouse models and human brain organoids. You will be involved in a diverse range of histological, cellular, and molecular techniques (including proteomics and transcriptomics approaches) to unravel the underlying mechanisms of this syndrome.
We offer a four-year pre-doctoral contract (Spanish Science Law) to work in a collaborative research environment, benefiting from the collective expertise and resources of the IBMB and the CRG. Intended Start Date, 16th October 2023.
Requirements:
- Acceptance into a PhD program: Applicants must be enrolled or accepted before September 29, 2023 into a PhD program in Biomedicine, Neuroscience, or related fields, in the 2023/2024 academic year.
- Passion for basic research and ability to work effectively in a collaborative team environment.
- Excellent written and oral English.
- Previous experience in molecular biology and mammalian cell culture is required. Experience in histology, confocal microscopy, and mouse work and knowledge of software such as Excel, GraphPad and PowerPoint are desirable.
How to apply:
If you meet the requirements, please send your CV, a motivation letter and 2 different contacts (email and phone) to ask for personal references to Mariona Arbonés (marbmc@ibmb.csic.es) or Susana de la Luna (susana.luna@crg.eu) before September 15th.
To learn more about our laboratories and ongoing research, please visit the following links:
Mariona Arbones
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6035-0235
Susana de la Luna
Offert for PhD student_IBMB-CRG